Introduction to Dango
EVM, Solana VM, Move, and CosmWasm, are the incumbent execution layers in the current landscape, all of which have their own unique weaknesses and strengths. As competitors, traditionally, a point of contention was always how fast they are, with, for example, SVM and Move being way faster than EVM. Competing to build a new, faster execution environment is probably not feasible, considering the efforts that have already been invested in the other environments. Still, a new kid on the block, Grug, is able to stand out by differentiating itself via its rich features. Although still in its infancy, Grug has already enabled the development of a new chain called Dango to start, and its upcoming features are very interesting. It is so interesting that we believe we should be paying attention. So, let’s dive in.
An Opportunity to Redefine Blockchain for DeFi

At its core, Dango’s core mission is to build a scalable, interoperable, and efficient blockchain infrastructure that is customised to the needs of developers, enterprises, and users. If successful, Dango would be able to truly stand apart from all other chains by distinguishing itself as a next-generation platform for dApps, especially because the current DeFi landscape is littered with capital inefficiency, cumbersome user interfaces, and rigid execution environments. Dango has this opportunity only because of Grug, and therefore, this warrants a quick overview of both Grug and Dango to make sure we have a complete picture.
Dango Meets Grug: A Synergy of Innovation
Built for flexibility and developer control, Grug is more than a traditional virtual machine. Grug has the ability to be intimately integrated with its blockchain infrastructure such that it is able to manage data flow, task scheduling and gas fee mechanism. It has the ability to act as an engine driving innovation and therefore Grug is able to power Dango’s most distinctive features.
So what is so special about Dango? 4 main features! Margin Accounts, Smart Accounts, Customizable Gas Fees and cronjobs. The Dango blockchain provides the decentralised, scalable and secure infrastructure required for all the operations occurring on the platform while, at the same time, it is able to handle large transaction volumes efficiently, maintaining decentralisation by leveraging a network of validators and also offering interoperability by seamlessly connecting to multiple blockchain ecosystems.
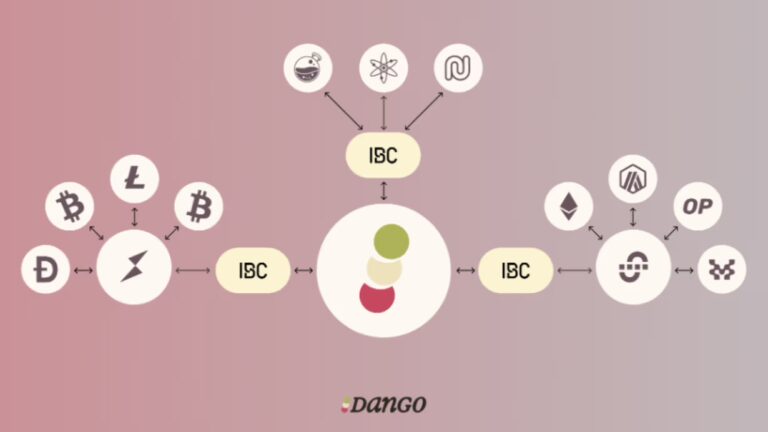
Let’s now have a deep look at Dango’s main features.
The Innovations Driving the Future of DeFi
Margin Accounts
What is it? Powered by Grug’s architecture, Margin Accounts offer users the possibility to unlock cross-collateralised leverage for trading, lending, and yield farming, therefore eliminating inefficiencies normally attributed to other collateral systems. In particle terms, this would effectively mean that a user would be able to deposit assets into a single account and make use of this collateral for multiple activities. For the sake of clarity, consider the following example where a user is able to make use of collateral which is already being used in perpetual futures trading to also support spot trading or lending.
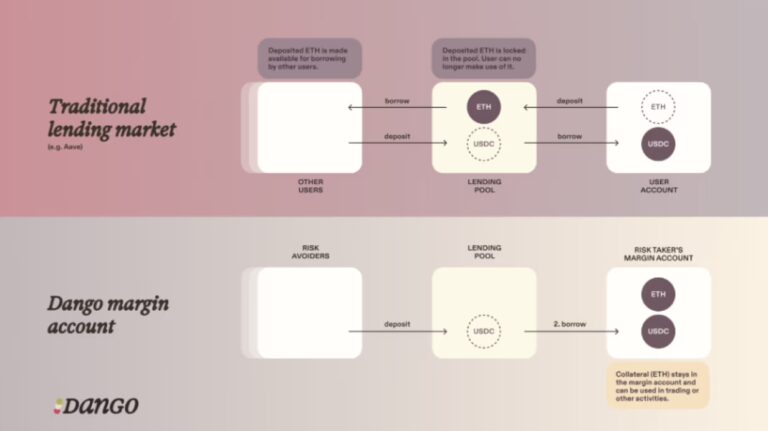
An important observation is that this architecture comes with additional inherent risks (as anything else in this industry), mainly because it opens up the possibilities for Cascading Liquidations. Essentially this means that multiple trading activities making use of the same collateral, amplifies the risks. If the value of the collateral drops, it may trigger a liquidation which may have a direct effect on other trading activities.
Smart Accounts:
Leveraging Grug’s execution environment, Smart Accounts are programmable accounts that support advanced transaction logic and authentication methods. This feature would enable developers to program customised logic for how transactions are executed, therefore opening up a new world of possibilities like biometric verification, Passkeys, and multi-factor authentication, enabling a key-less wallet experience.
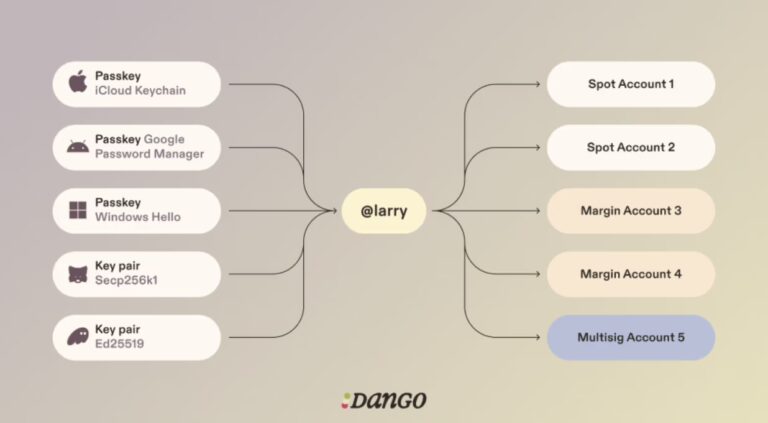
The project’s endgame is to offer a key-less wallet experience. Instead of having to self-custody your private key, making use of Smart Accounts, you would be able to generate and store a private key in the cloud and therefore making it accessible from any device while at the same time, it would still give you full control by making use of biometrics to sign transactions. It is easy to see how such architecture would significantly lower the barrier to entry for new users, as it drastically simplifies private key management.
Customizable Gas Fees
Traditional platforms often have rigid gas fee systems, and often, they employ a one-size-fits-all model, are dependant on hard forks to implement changes and offer limited customisation to developers. For example, building a dAapp on Ethereum does not allow developer control on fee distribution, discount offerings and incentivisation.
Dango allows for dynamic and programmable gas fee mechanisms by introducing the Taxman smart contract. This smart contract empowers developers to implement any logic related to gas fee-burning, allows for fee discounts to be attributed to specific groups of users, and allows for tailored fee structures, all without the need for any hard forks. Just as an example of one use case, imagine a gaming ecosystem that makes use of this feature to give gas fee discounts for having a particular NFT.
Cron Jobs
Cronjobs may be considered as one of the standout features of the project. Essentially, these are on-chain automated task schedulers that automatically are able to execute predefined operations as previously programmed by developers. Without needing manual intervention or any external triggers, through cronjobs, Dango is able to reduce its dependency on external bots or centralised services, therefore acting in a cost-effective and reliable manner.
One of the multiple use cases cronjobs have is within DeFi protocols, for example, by having funding rates within perpetual future protocols to be updated at set intervals without relying on external infrastructure. Although, in this case, an oracle (e.g. Chainlink) would still be required to retrieve off-chain market data, cronjobs would be able to trigger oracle updates automatically and, at the same time, process the data to calculate the new funding rates.
Bonus Feature: A New Token Standard
Although not directly related to Dango itself, Grug enables the creation of a new token standard that addresses many of the severe limitations of ERC-20. The new token standard promises to enable the transfer of multiple tokens in a single transaction, introduce atomic token interactions, which would eliminate the risk of infinite approvals, address transfer rejection, prevent accidental loss of funds and also combine fungible tokens and NFTs into a single token standard.
Tokenomics
Dango’s native token will be DNG, and it will play a pivotal role within the ecosystem. The total supply of the token will be that of 30,000.

Unlike most other chains, the DNG token will not be used to pay for transaction fees. Instead, Dango operates a USDC standard, meaning that all transaction fees are paid in USDC. Considering that all the fees are collected and used to buy back and burn DNG tokens, this creates a deflationary pressure on DNG’s circulating supply and, therefore, would probably have a positive effect on the value of each token. Furthermore, although not outlined specifically within the current Dango documentation, it seems that DNG holders will also have the ability to vote (eventually), at least on additional fee switches.
What should definitely be highlighted at this stage is that, as you might have noticed, there won’t be any staking mechanisms. It is the project’s belief that users usually do not like to stake or lockup their tokens. Therefore, the natural question to ask is how the Dango chain is secured. Dango will be making use of a proof of authority validator set which will be composed of around 20 nodes which are chosen by the Left Curve Foundation. Interestingly, this is a similar setup to the Binance Smart Chain. Furthermore, in contrast to most other chains, validators will have no say in governance, will not be able to take delegation of tokens and will not earn any revenue from on-chain activity. Instead, the Left Curve Foundation will essentially be billed for the operating costs, while all the revenue generated by the change will go to token holders and affiliated marketers.

The project is planning to do an ICO, which is in compliance with the MiCA framework, and the current plan is to distribute as shown in the diagram below.
Recent Developments and Roadmap
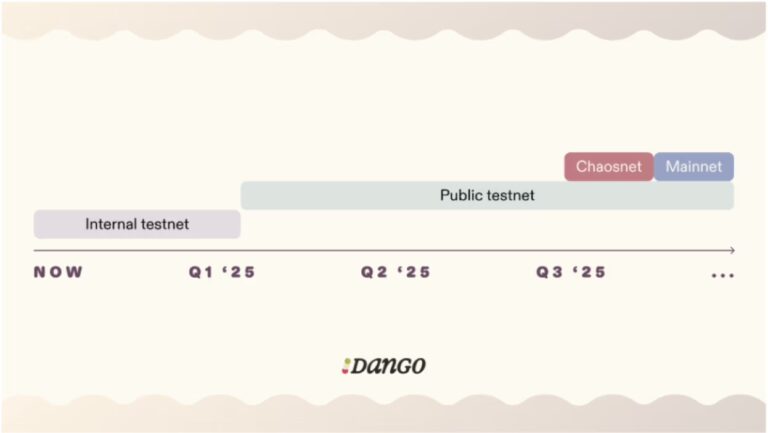
Dango is still in the development phase and is currently focused on internally testing the testnet, with plans to launch a series of public demo-nets, each with incrementally more features in the future as per the following timeline.
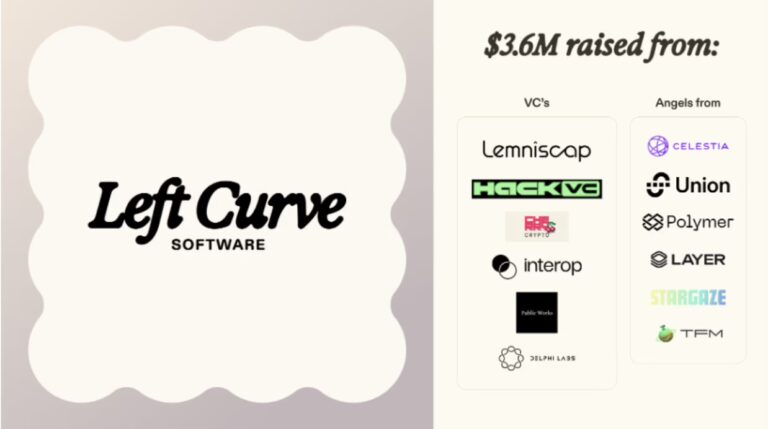
What is notable is that this development is supported by various VCs and Angel investors. Lemniscap and Hack VC co-lead a $3.6M seed round with the participation of Cherry Crypto, Interop, Public Works, Delphi Labs and more.
Conclusion
Although it is very early days, Dango seems to be an exciting project worth keeping an eye on. It’s unique architecture distinguishes it from the rest and has the potential to foster an ecosystem of innovative technologies. It is hard to say if the project will be successful in delivering on its ambitious goals, but what is certain at this stage is that the potential is clear.
Additional Resources
Dango Website: https://grug.build/index.html
Dango X: https://x.com/dango_zone
Grug Whitepaper: https://grug.build/whitepaper.html

(Terms & Conditions Apply)
About Simply Staking
We are a Blockchain Services Provider who operates Validators and Nodes on over 30 Networks with over $1 Billion in Assets Staked. Our journey started in 2018, with Simply entering the Cosmos Hub Testnets, and now have expanded our operations to most major ecosystems including networks such as LIDO, Polygon, EigenLayer, Oasis Network, Cosmos Hub, Polkadot, and many more, all while being an Oracle Operator on Chainlink.
We offer additional services such as Nodes-As-A-Service (RPCs), Blockchain Development work, Tooling, Governance Services as well as Blockchain Consultancy Services.
More Information on our offerings can be found on our website.
Disclaimer: This article contains affiliate links. If you click on these links and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. These commissions help support our work and allow us to continue providing valuable content. Thank you for your support!
Terms & Conditions apply on all partnership offers.
This article is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Investing in cryptocurrencies carries significant risks and is highly speculative. The opinions and analyses presented do not reflect the official stance of any company or entity. We strongly advise consulting with a qualified financial professional before making any investment decisions. The author and publisher assume no liability for any actions taken based on the content of this article. Always conduct your own due diligence before investing.