A recap on Berachain
Berachain is an EVM-compatible blockchain powered by a unique Proof-of-Liquidity (PoL) consensus mechanism. Its goal is to align network incentives by integrating validators and ecosystem projects more effectively through an economic model designed to boost liquidity and governance.
The platform’s Polaris framework enables the creation of modular, EVM-compatible chains on top of the CometBFT consensus engine. This approach enhances blockchain design, focusing on efficient trading, price stability, and network growth, while also supporting decentralised application (dApp) development and broader user adoption.
For a full refresher on Berachain’s fundamentals see our introductory article.
For the rest of this piece, we cover the following topics:
- Berachain Testnet 1 and Testnet 2
- Berachain Reward Vaults
- Economics of Incentives
- Governance on Berachain
- BEX – Berachain DEX
- Current traction & ecosystem projects
Berachain Testnet 1 and Testnet 2
On June 9, 2024, Berachain launched version 2 of its testnet, bArtio, further rolling out the modular architecture and facilitating a stronger alignment with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) standards. To facilitate these improvements, a new framework called BeaconKit was introduced. To this end, several key architectural changes were made in Berachain’s transition from V1 (Artio) to V2 (bArtio). V1 was built using Polaris, which tightly integrated EVM execution with the Cosmos SDK in a monolithic framework, focusing on precompile optimisations but facing limitations.
By way of introduction, Polaris is an innovative framework designed to simplify the integration of an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) into app chains or dApps. Polaris is built with an easy-to-integrate API that eliminates the need for developers to spend time hacking their own EVM integration solutions together. The framework is highly modular, allowing projects to choose the components that best fit their needs and integrate an EVM environment into virtually any application.
The core components include:
- Build: Developer tooling and scripts that are essential for automating development tasks, compiling code, and managing the software deployment process.
- Cosmos: Polaris integrated with the Cosmos-SDK allowing for a seamless interaction with other Cosmos-based blockchains by enabling interoperability, scalability, and the utilization of Cosmos’ Tendermint consensus engine.
- Contracts: Smart contracts and bindings ensure that various functions like token transfers or governance decisions are executed without the need for intermediaries
- ETH Core: Main EVM components which allow Etehreum-familiar devs to leverage the same tools and environment, promoting broader adoption and application development
- e2e Testing: End-to-end (e2e) testing utilities are designed to ensure that all system components work together as expected. These tools help validate the full flow of operations from start to finish, ensuring that new updates or changes do not break any functionality and that the system remains secure and efficient.
Any developer can set up a local network with Go and Foundry for testing purposes. But to do this, you would need to access testnet tokens – you can do so through our Berachain Faucet allowing you to bootstrap your testnet wallet! See more information on how to use the faucet and access testnet BERA tokens for free here.

Despite constructive utility, One major challenge with Polaris was that the Cosmos SDK couldn’t handle the transaction volume Berachain received. Additionally, the forked EVM client had compatibility issues. As a result, V2 moved to a more modular framework (BeaconKit) to better align with EVM standards and address these scaling challenges.
| Execution Client Comparison | ||
|---|---|---|
| Aspect | Polaris (V1 Artio) | BeaconKit (V2 bArtio) |
| Execution Client | EVM (Forked w/ Cosmos Precompiles) | EVM (Geth, Reth, Erigon) |
| Consensus Algo. | CometBFT | CometBFT |
| Finality | Single Slot (Instant) | Single Slot (Instant) |
| Architecture | Monolithic | Modular |
Berachain’s V2 introduced a modular architecture by separating the consensus and execution layers. Unlike V1, where validators ran a single Polaris client, V2 validators now run two clients: the BeaconKit client (for consensus) alongside any EVM execution client (e.g., Geth or Erigon). This modular design enables the execution layer to adopt innovations from the broader EVM ecosystem while allowing BeaconKit to provide a flexible, high-performance consensus layer.
The advantages of BeaconKit can be boiled down to 4 key aspects:
- Single Slot Finality: Blocks reach finality instantly, a significant improvement over Ethereum’s ~13-minute finality time.
- Optimistic Payload Building: Block proposals and voting occur in parallel, reducing block times by up to 40%, and enhancing speed and efficiency.
- Conformity to Eth2 Modularity: The architecture is designed to match Ethereum’s modularity, enhancing compatibility and flexibility.
- Full EIP Compatibility: Supports Ethereum Improvement Proposals, ensuring seamless EVM execution and updates.
In parallel, V2 also features an updated economic model for Berachain’s native tokens, enhancing the overall design of the network. The following table highlights the main changes between V1 and V2:
| Validator System Comparison | ||
|---|---|---|
| Topic | V1 | V2 |
| Validator Bond | BGT (Low Amount) | BERA (69,420) |
| Slashing | BGT Delegators (Pro Rata) | ONLY Validators (Activation BERA) |
| Rewards Weighting | Delegated BGT | Delegated BGT |
| Block Production | BGT Delegation Weight = Block Production Rate | All Validators = Equal Chance For Block Production + BGT Delegation Weight = Emissions |
| Architecture | Polaris | BeaconKit |
| Validator Limit | 100 | 128 (Potentially More) |
As a result of V1 to V2 upgrade, moving forward, $BERA is staked for activating validators, rather than $BGT and $BGT delegators are no longer at risk of slashing risk while the execution layer is now EVM identical.
Berachain Reward Vaults
Reward vaults are smart contracts where users stake Proof of Liquidity (PoL) eligible assets to earn $BGT rewards. These vaults serve as the exclusive mechanism to earn $BGT, thus acting as the gateway into the PoL ecosystem. They enable protocols to incentivise user behaviour by offering rewards in exchange for staked assets, where each protocol can operate multiple reward vaults, each tied to a specific PoL-eligible asset. For instance, BEX could run various vaults, each with its own pool and respective asset, all earning $BGT.
In order to receive BGT, a user must be staking the PoL-eligible asset in its reward vault. The protocol that deployed the reward vault can decide how the user acquires the PoL-eligible asset to stake. The idea is that protocols would leverage this to attract liquidity or stimulate activity, and in return award users with the asset they can stake in their vault.
- The user takes some action that results in receiving a PoL-eligible asset, generally referred to as a receipt token.
- The user stakes the PoL-eligible asset in the corresponding vault.
- The user earns a portion of all the BGT emitted to that vault.
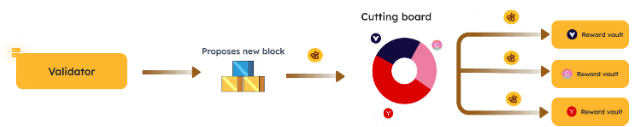
The user and validator interaction through the vault is showcased in the image below:

The amount of $BGT rewards a user earns from a reward vault depends on:
- The user’s proportion of the total assets staked in the vault
- The amount of $BGT rewards allocated to that vault
After staking, users can claim rewards, add more assets, or withdraw at any time. This reward system is designed to mimic familiar DeFi actions, making $BGT farming accessible to regular users with a low entry barrier.
BGT’s Journey to Reward Vault
| Name ???? | Description ???? | Link ???? | Social ???? | Type ???? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GummiFi | multi-asset money market | https://www.gummi.fi/ | https://x.com/GummiFi | Spotlight |
| Kodiak | Berachain native liquidity hub | https://www.kodiak.finance/ | https://x.com/KodiakFi | Spotlight |
| Berabot | Telegram trading & sniper bot on Berachain | https://twitter.com/Berabot_ | https://twitter.com/Berabot | DeFi |
| BurrBear | one-stop Stablecoin + RWA shop for the Berachain | https://www.burrbear.io/ | https://x.com/moneygoesburr | RWA |
| Beraborow | interest-free loans backed by iBGT, issued in stablecoin | https://twitter.com/beraborrow | https://twitter.com/beraborrow | DeFi |
| Nitro | Cross-chain bridge by Router Protocol | https://nitro.routerprotocol.com/ | https://twitter.com/routerprotocol | Bridge |
Validators can direct some portion of their $BGT emissions to specific reward vaults of their choice.
Validators in the Berachain ecosystem could choose to emit $BGT to a particular reward vault because of three main reasons:
- Incentive Alignment: Emitting $BGT to specific vaults helps align incentives between validators and the community, encouraging participation in initiatives critical for ecosystem growth.
- Supporting Liquidity: Validators can enhance liquidity by rewarding vaults designed to facilitate efficient trading, attracting liquidity providers to the ecosystem.
- Community Governance: Emitting rewards to particular vaults fosters community engagement in governance, encouraging users to participate in decision-making processes and strengthening decentralisation.
New Reward Vaults can be created without permission, but they must undergo a Whitelisting process governed by $BGT holders to qualify for receiving $BGT emissions from validators.
The qualification process ensures that only vetted vaults are approved for rewards.
Moreover, developers or protocols interested in creating a new reward vault for a specific Proof of Liquidity (PoL)-eligible asset can submit a proposal for whitelisting and If this proposal is approved by the governance community, the vault’s address is added to a list of approved reward vaults. Once on this list, validators can direct their $BGT emissions to the newly whitelisted vault.
Governance on Berachain
Berachain’s governance system empowers token holders, via $BGT, to make key decisions affecting the protocol and its core decentralised applications (dApps). Holders can influence important aspects like Proof of Liquidity (PoL), whitelisting new staking assets, adjusting $HONEY minting parameters, and modifying the governance models for native dApps like Bend (Berahcains native lending protocol).
During the testnet phase, the governance process begins with Proposal Creation, where any user with sufficient $BGT can propose changes. After submission, the proposal enters a Pending State, a waiting period before voting opens.
During the Active Voting phase, $BGT holders can vote on the proposal. For a proposal to pass, a quorum of $BGT must be met, and the Proposal Outcome is determined as either Succeeded or Defeated. If successful, the proposal enters a Timelock, a delay before execution. Finally, the proposal is implemented after the timelock period expires.
To submit a proposal, the user needs to delegate their $BGT, prepare a detailed proposal, and use the governance contract to submit it on-chain. The entire process includes monitoring and encouraging community participation to ensure the proposal passes.
| Governance Metrics | |
|---|---|
| State | Criteria |
| Proposal Creation | 1000 $BGT Required |
| Pending State | 3-hour waiting period |
| Active Voting | 3-hour voting period |
| Proposal Outcome | 2BN $BGT required to reach quorum |
| Timelock | 3-hour delay |
BEX – Berachain DEX
BEX (Berachain Exchange) is Berachain’s native decentralised exchange (DEX) protocol, allowing users to trade any pair of crypto assets directly on-chain, without intermediaries and it is available on Berachain’s bArtio testnet: BEX bArtio.
BEX functions through an Automated Market Maker (AMM) system. Instead of traditional order books, it uses liquidity pools where assets are traded against one another. As trades occur, the price of the assets in the pool adjusts, establishing a new market rate for each asset.
BEX runs entirely within a single smart contract, making it highly efficient and lightweight. It draws inspiration from innovations pioneered by Ambient Finance.
BEX’s architecture provides several advantages over traditional DEXs:
- Optimized Gas Efficiency: Reduces gas costs significantly compared to other DEXs
- Full-Range Liquidity (Uniswap V2-style): Each liquidity pool uses a wide range of liquidity for simplicity and efficiency in trading
- Pre-funded Tokens: Users can pre-fund tokens as “surplus collateral,” improving the efficiency of active traders by deferring token transfers until final settlement
- Gasless Transactions (EIP-712): Supports off-chain transactions using the EIP-712 standard, allowing users to pay gas fees in the swapped token instead of ETH or other base assets.
- Account Abstraction: Empowers users to submit off-chain orders and define custom logic for order fulfilment by relayers
- Permissioned Pools: Offers unique “permissioned pool” functionality, enabling governance and restrictions using smart contract oracles, allowing customised pool control
Overall BEX’s native architecture, coupled with innovative features like pre-funded tokens and industry standards like the full range liquidity streamlines trading while giving users flexible, advanced features for efficient and secure DeFi.
Current traction & ecosystem projects
Berahcain hosts several unique, utility and yield-driven projects ranging from money markets to real-world assets and bridges.
Highlights include projects like BurrBear – a one-stop Stablecoin and RWA shop for the Berachain as well as GummiFi a multi-asset money market protocol.
Below you can see a snippet from an extensive Berachain ecosystem table that we have created for you. You can access the complete table here.
As for testnet traction, Berachain has seen significant and stable growth in key on-chain metrics such as the count of transactions and the number of unique addresses.
As shown below, transactions grew from 225,000 on June 2024 to 5,556,00 by October 16, 2024, with major upside coinciding with testnet announcements and partnerships.
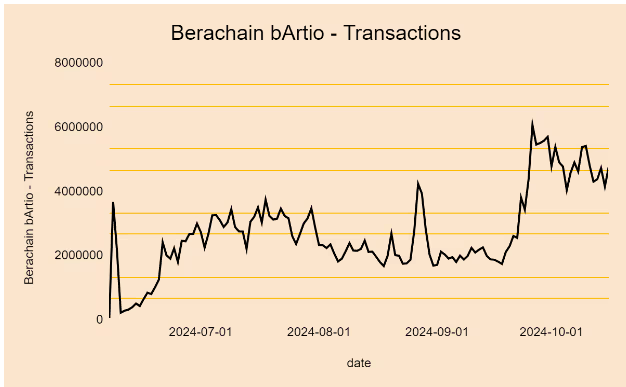
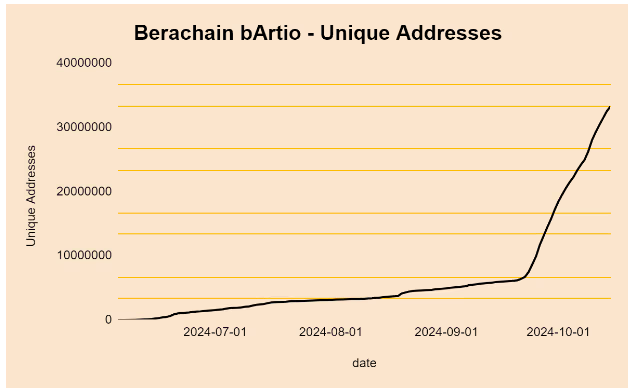
As shown in the graph below, the number of unique addresses on Berahcain is in line with the growth trend of the number of transactions, with the unique addresses spiking after the release of the V2 testnet and currently sitting at over 33 million.
Besides, Berachain testnet has processed 360 million transactions and finalised 5,682,156 blocks, thus successfully testing its finality and transaction processing capabilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Berachain’s technical advancements have positioned it as a powerful EVM-compatible blockchain driven by its unique Proof-of-Liquidity (PoL) consensus mechanism. The transition from Polaris (V1) to BeaconKit (V2) brought about a more modular architecture, enhancing scalability, performance, and EVM compatibility. This modular approach allows for seamless integration with various execution clients, optimizing gas efficiency, liquidity, and user experience. With innovations like BEX, reward vaults, and governance systems, Berachain is building an interconnected ecosystem, fostering an end-to-end ecosystem for easy dApp development and offering sustainable staking mechanisms. The consistent growth in transactions and user adoption during the testnet phase reflects the platform’s potential for further growth and development.

(Terms & Conditions Apply)
About Simply Staking
We are a Blockchain Services Provider who operates Validators and Nodes on over 30 Networks with over $1 Billion in Assets Staked. Our journey started in 2018, with Simply entering the Cosmos Hub Testnets, and now have expanded our operations to most major ecosystems including networks such as LIDO, Polygon, EigenLayer, Oasis Network, Cosmos Hub, Polkadot, and many more, all while being an Oracle Operator on Chainlink.
We offer additional services such as Nodes-As-A-Service (RPCs), Blockchain Development work, Tooling, Governance Services as well as Blockchain Consultancy Services.
More Information on our offerings can be found on our website.
Disclaimer: This article contains affiliate links. If you click on these links and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. These commissions help support our work and allow us to continue providing valuable content. Thank you for your support!
Terms & Conditions apply on all partnership offers.
This article is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Investing in cryptocurrencies carries significant risks and is highly speculative. The opinions and analyses presented do not reflect the official stance of any company or entity. We strongly advise consulting with a qualified financial professional before making any investment decisions. The author and publisher assume no liability for any actions taken based on the content of this article. Always conduct your own due diligence before investing.