What is Berachain?
Berachain is an innovative blockchain designed to enhance decentralised finance (DeFi) by offering a more efficient and user-friendly platform. Unlike traditional blockchains, Berachain introduces a unique system where users can participate in securing the network by staking their assets, similar to earning interest in a savings account. This staking mechanism not only helps maintain the security of the network but also rewards users for their participation.
What sets Berachain apart is its focus on creating a more integrated and rewarding environment for DeFi applications. Berachain aims to make it easier for developers to build and for users to engage with DeFi services, all while ensuring a secure and scalable platform.
Berachain is EVM-identical, reaches consensus via a system called Proof of Liquidty (POL) and has a 3-token ecosystem. Stick with us as we break down Berahcain’s key components.

Beranchain’s EVM Resemblance
Berachain’s execution layer functions in the same way as the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) runtime environment on the Ethereum Mainnet.
To clarify, the execution layer is the part of the blockchain that processes transactions and executes smart contracts, while the runtime environment is where these smart contracts actually run. Berachain uses the same unmodified execution clients—software like Geth, Reth, Erigon, and Nethermind—that handle the actual execution of these contracts. Because of such an EVM-identical structure, all the tools and resources designed for the EVM on Ethereum work seamlessly with Berachain as well.
Since Berachain’s execution layer mirrors the EVM, it can easily adopt any updates made to the EVM. For example, when a new Ethereum version like “Dencun” is released, Berachain can incorporate this update without needing any changes. This compatibility includes all Remote Procedure Call (RPC) namespaces and endpoints, so any improvements made to the EVM clients—these are the programs that interact with the blockchain—will directly enhance Berachain’s performance as well.
Proof of Liquidty:
It is interesting to see that despite Berachain mirroring Ethereum’s Virtual Machine (VM) and programmability capacities, it does not do so when it comes to consensus mechanisms.
Before we dive into Berahcain’s Proof Of Liquidty (POL), we should first understand what are the challenges associates with Ethereum’s consensus mechanism, also known as Proof of Stake (POS).
Understanding the Challenges of POS
PoS is a consensus mechanism that has its strengths, but it also presents certain limitations, particularly in how it fosters collaboration among the various participants in a blockchain ecosystem. Validators, who play a crucial role in maintaining the network, often have minimal interaction with the protocols and end-users that rely on the infrastructure they support. Despite this, validators receive most of the economic benefits from the network.
To create a healthier and more balanced ecosystem, it’s essential that projects, validators, and the broader blockchain network work together to share in the network’s growth. This is where Proof-of-Liquidity (PoL) comes in.
What is Proof-of-Liquidity (PoL)?
Proof-of-Liquidity (PoL) is a consensus model that ensures the active involvement and collaboration of all the chain’s stakeholders. In a PoL system, different participants must work together to maximise the liquidity on the chain, which in turn ensures that they all benefit from the network’s growth and success.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how Proof-of-Liquidity operates, particularly focusing on the roles of validators and liquidity providers:
- Initial Participation: A prospective validator starts by providing a bond in the form of the chain’s gas token (in this case, $BERA). This bond secures the network and makes the validator eligible to produce blocks
- Block Proposal: Validators who are active on the network have an equal opportunity to be randomly selected to propose a block
- Reward Distribution: When a validator successfully proposes a block, the network rewards them with a governance token ($BGT), which the validator can then distribute.
- Allocation to Reward Vaults: The active validator decides how to distribute the $BGT among various Reward Vaults. These decisions are governed by the Berachef contract, which includes a list of addresses and the percentages allocated to each vault.
- Liquidity Provision: Liquidity providers contribute to the network by adding liquidity to pools, such as depositing tokens like $HONEY and $BERA into a liquidity pool
- Receipt Tokens and Staking: In return for providing liquidity, liquidity providers receive a receipt token that can be staked in the Reward Vaults, making the provider eligible to claim $BGT based on their contribution.
- Becoming a BGT Holder: Once the $BGT tokens are distributed to the Reward Vaults, liquidity providers can claim them, becoming BGT Holders
- Delegating BGT: BGT Holders can delegate their $BGT tokens to an active validator, turning them into a Boosted Validator. More delegation increases the rewards that the validator can distribute when they propose a block, hence benefitting the delegators further.
A summary of the above steps is represented by the diagram below:
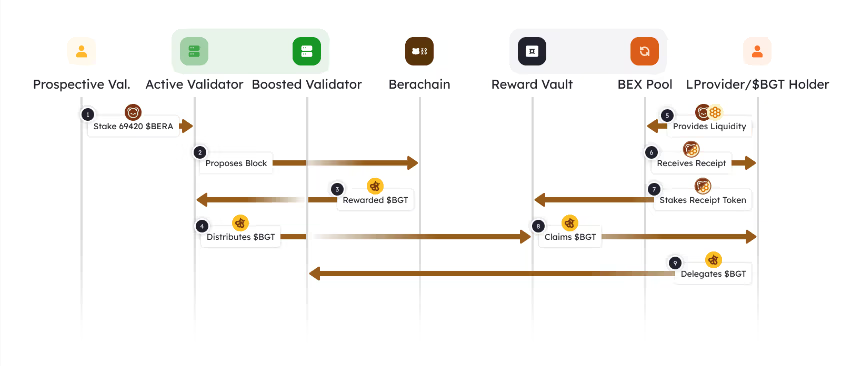
(Source: Berachain Docs)
Aligning Protocols and Validators
The PoL model introduces a new dynamic where validators have the responsibility of distributing governance tokens (like $BGT) to Reward Vaults, therefore fostering a system with a stronger relationship between validators and the ecosystem’s protocols. The more governance tokens a validator can gather through delegation, the greater their reward distribution capability, creating a mutually beneficial relationship.
Protocols can also incentivise validators to direct rewards toward their specific vaults by offering additional benefits, ensuring that validators have a vested interest in supporting those protocols.
Here are some examples of how Reward Vaults are currently implemented in the Berachain ecosystem:
- BEX – Involves specific BEX Pools
- Berps – Allows for depositing $HONEY into Berps Honey Vault
- Bend – Enables borrowing $HONEY
This overview illustrates how Proof-of-Liquidity can drive collaboration and growth within a blockchain ecosystem by aligning the incentives of all participants.
Participants:
As every other blockchain ecosystem, Berachain fosters multiple types of participants including Validators, Token Holders & Farmers, the Bera Foundtion and Ecosystem Projects – each of them playing a crucial role and keeping the ecosystem sustainable.
Validators
Validators in the Berachain ecosystem are responsible for reaching consensus on the blockchain’s state. They earn rewards by staking $BERA tokens, which can be slashed for misbehavior. Validators earn through gas fees, priority fees, and commissions on $BGT rewards, incentivising collaboration with protocols and strategic alignment to attract $BGT delegations from holders by demonstrating profitable reward distribution.
$BGT Holders & Farmers
$BGT holders play a double role of governance and influencing reward distribution through delegation to validators. Farmers, seeking $BGT rewards, look for the most profitable Reward Vaults based on their risk profiles. By delegating $BGT to validators directing emissions to favorable Reward Vaults, they can boost their rewards. Meanwhile, Holders benefit by delegating to validators that maximise returns from Reward Vaults, promoting economic efficiency across the network.
You can simply stake and secure your assets with the Ledger wallet.
Bera Foundation
The Bera Foundation operates default decentralised applications (dApps) like Bex, Bend, and Berps, which generate fees for $BGT holders. These dApps are pre-established by the foundation to offer key services to users, provide liquidity and serve as default Reward Vaults until new protocols are integrated. The foundation ensures there is intrinsic demand for $BGT, maintaining a stable economic foundation within the Berachain ecosystem, independent of external incentives.
Ecosystem Projects
Protocols within Berachain (which we will review in the upcoming Berachain deep dive) can leverage the PoL system to bootstrap liquidity by aligning with validators and $BGT holders. They incentivise validators to direct $BGT emissions to their Reward Vaults, effectively competing to attract deposits, thereafter creating a positive feedback loop where increased $BGT value leads to higher token value for projects providing incentives. New projects must earn support from $BGT holders to integrate into the PoL system, aligning their success with the broader ecosystem’s growth.
If you are one of those who is looking to build on Bera, you will definitely need some $BERA tokens for the testnet. Don’t worry, we got you – use your Berachain faucet-as-a-service, and if it’s your first time interacting with faucets, we got you here as well – check our Bera Faucet Guide!
Now that we covered the EVM resemblance, POL and Participants, its finally time to fully uncover Bera’s tri-token system.
3-token Ecosystem
Berachain is uniquely positioned in borth within and outside EVM due to it’s tri0token ecosystem taht includes $BERA, $BGT and $HONEY. To find out what functions each token is designed for, follow our breakdown below!
$BERA Token
The $BERA token is used for two main purposes on the Berachain network:
- Transaction Fees (Gas Token): $BERA is used to pay for transactions on the blockchain. This payment is often referred to as a “gas fee.”
- Staking for Validator Nodes: By staking $BERA, users can help activate validator nodes. The combined value of all staked $BERA tokens forms the base layer of the network’s security. Additional security is provided by $BGT, which builds on top of this layer.
$BGT Token
In traditional Proof of Stake blockchains, a single token often handles multiple roles, including staking, governance, and providing economic incentives. However, Berachain uses a unique three-token system called the Proof of Liquidity model, which separates these functions.
- Governance: $BGT is the governance token on Berachain. It is used to vote on network decisions and proposals. Holders of $BGT can vote directly or delegate their voting power to others
- Earning Incentives: Validators can earn rewards based on how much $BGT is delegated to them. More delegations usually mean higher rewards, incentivising validators to perform well
- Burning for $BERA: $BGT can be burned (permanently destroyed) in exchange for $BERA on a 1:1 basis. Once converted, $BERA cannot be turned back into $BGT
$BGT is not transferrable like regular tokens and can only be earned through specific actions, such as providing liquidity in eligible assets. For example:
- Depositing liquidity in the native Bex exchange
- Borrowing or lending the $HONEY stablecoin in Berachain applications like Bend
$HONEY Token
$HONEY is Berachain’s stablecoin, designed to maintain a stable value pegged to 1 USD. Unlike other cryptocurrencies, which can be highly volatile, stablecoins like $HONEY are intended to offer price stability. $HONEY has multiple use-case, including:
- Lending: Users can lend $HONEY on platforms like Bend to earn interest. In return, they receive a token like $aHONEY, representing their deposited amount.
- Borrowing: $HONEY can be borrowed against other assets provided as collateral.
- Perpetual Futures Trading: On Berachain’s Berps platform, $HONEY serves as the base token for all trading activities. Traders deposit $HONEY to open positions, and liquidity providers can earn fees by staking $HONEY in the $bHONEY vault.
Overall, the three tokens create symphony between stability, security and incentives. $BERA is used for transaction fees and staking to secure the network, $BGT is the governance token for voting and earning rewards, and can be burned for $BERA, while $HONEY is a stablecoin used for lending, borrowing, and trading within the Berachain ecosystem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Berachain’s compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) provides a seamless experience for developers while its tri-token system ($BERA, $BGT, and $HONEY) ensures economic sustainability, with token playing a specialised role in maintaining the ecosystem’s stability, security, and incentivisation. With validators securing the network through $BERA staking, $BGT guiding governance and rewards, and $HONEY providing price stability for DeFi applications, Berachain’s design is offering a scalable and user-friendly platform for participants.
Berachain introduces a dynamic ecosystem that aligns the interests of all participants, to facilitate collaboration between validators, liquidity providers, and protocols. Its PoL model offers a unique incentive structure that not only enhances network security but also rewards validators and $BGT holders through strategic participation in liquidity pools and governance. By distributing $BGT emissions to Reward Vaults, validators strengthen their relationship with ecosystem projects, further driving liquidity and overall growth. Collaborative structure sits at the center of Berachain, ensuring that each participant benefits from the network’s success and creating a symbiotic environment.
Disclaimer: This article contains affiliate links. If you click on these links and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. These commissions help support our work and allow us to continue providing valuable content. Thank you for your support!
This article is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Investing in cryptocurrencies carries significant risks and is highly speculative. The opinions and analyses presented do not reflect the official stance of any company or entity. We strongly advise consulting with a qualified financial professional before making any investment decisions. The author and publisher assume no liability for any actions taken based on the content of this article. Always conduct your own due diligence before investing.