Base is a Layer 2 scaling solution whose ambition is to bring the next billion users on-chain. Developed and supported by Coinbase, Base leverages the Optimism (OP) Stack to provide a secure, low-cost, and developer-friendly environment for building dApps. With strong backing, seamless integration with Coinbase products, and a clear roadmap toward decentralisation, Base is positioning itself as a key player in Ethereum’s scaling ecosystem, and therefore the case for a deeper dive from our end is evident!
What is Base?
Developed using the OP Stack, Base may be defined as a Ethereum Layer 2 scaling solution that provides a secure, low-cost, and developer-friendly environment for building on-chain applications. Unlike most other L2s, Base has committed not to have its own native gas token; instead, it uses ETH to fulfil this purpose.
Coinbase (founded in 2012), mostly known within the industry for being one of the biggest centralised crypto exchanges, announced the launch of Base’s testnet in February 2023 as an extension to Coinbase’s core values of building a future where financial systems increase economic freedom globally. While leveraging the company’s extensive experience within the industry, Base serves as Coinbase’s on-chain home. The Layer 2 blockchain provides developers with seamless integration with Coinbase’s products and liquidity, and although initially developed by Coinbase itself, Base is committed to progressive decentralisation, aiming to become a public good rather than a Coinbase-controlled project.
Base’s primary goal is to be a catalyst for bringing billions of users to Web3, therefore making on-chain the next online.
The Tech Behind Base
The project was initially built and developed in partnership with the Optimism Collective, a group of companies, communities and individuals who work together to reward initiatives that are trying to build a sustainable future for Ethereum. Base is built on the OP Stack, which enables it to batch and compress transactions before settling them on the Ethereum mainnet, reducing costs while maintaining security. But what is the OP Stack? Well, it is an open-source, modular framework that is designed to power Ethereum Layer 2 rollups, and by using it, Base also ensures high interoperability with other Layer 2s built using the same framework, such as Optimism itself.
Base’s Security
It should be noted that another key benefit of making use of the OP Stack is that, right from the start, Base could leverage all the security work that was done before by the OP Labs team and also the Optimism community. Not only that but to ensure maximum security, Coinbase commissioned an internal audit of the stack to further ensure its resilience by auditing all pre-deploys and contracts both on Layer 1 and Layer 2, testing critical components like L2 bridges and sequencers, creating operational runbooks for various scenarios and situations that can least to certain distress events, while evaluated and verified the key management framework and smart contracts for Base.
The Superchain

Base’s architecture is part of the broader Superchain vision, that of being a network of OP Stack-based Layer 2s that share security and communication protocols. This approach closely resembles Cosmos’ interchain model, where independent blockchains operate seamlessly within a unified ecosystem. The Superchain aims to reduce fragmentation in the Layer 2 space by enabling interoperable rollups, allowing transactions between different chains to be efficient, low-cost, and decentralised while inheriting Ethereum’s security.
Instead of multiple isolated Layer 2 solutions, the Superchain fosters a cohesive network of rollups, offering an integrated alternative to the current landscape. Several projects have already embraced this vision, including opBNB, an OP Stack-powered Layer 2 designed to scale Binance’s ecosystem, and Soneium, Sony’s blockchain initiative aimed at bridging Web2 and Web3 experiences. These projects, along with Base, demonstrate the growing adoption of the Superchain model, reinforcing a future where Ethereum Layer 2s operate as an interconnected, unified network rather than standalone solutions.
Now that we understand Base’s foundations let’s take a few moments to understand the rationale behind not issuing its own network token!
ETH as a Gas Token
The decision not to introduce its own token for transaction fees is not common for most layer 2s, but why was the decision taken? First of all, by doing so, the project prioritised Ethereum-native integration by not launching its own speculative asset. At the same time, not having a new token eliminates many regulatory risks and ensures compliance, especially considering the deep connections Base has with Coinbase. Furthermore, by making use of ETH as the native gas token, it keeps transaction costs predictable and maintains a direct link to Ethereum’s economic model.
Recent Tech Developments: New Building Blocks to Enhance Base
In a recent blog post, Base introduced three key enhancements to its tech stack which pushes the project closer to achieving its long-term goals.
Key Enhancement 1: Flashblocks: Making Base 10x Faster
Inspired by Solana’s Shreds, which break transaction data into smaller, efficiently processed chunks to accelerate block propagation, and Celestia’s Data Squares, which optimise data availability through sampling rather than full block downloads, Flashblocks is designed to enhance Ethereum rollups for speed and efficiency. While optimising for Ethereum’s architecture, Flashblocks reduces block times from 2 seconds to 200 milliseconds, making Base the fastest EVM chain. Although not yet live on mainnet, Flashblocks are already available on Base Sepolia testnet, with a targeted mainnet launch in Q2 of 2025.
For a deep technical dive on Flashblocks, we suggest reading this on GitHub.
Key Enhancement 2: Base Appchains: Layer 3 Scaling for High-Traffic dApps
To help Base scale further, Appchains were introduced as Layer 3 chains, which can provide dedicated blockspace for dApps. dApps which spend significant funds on gas sponsorship will find Appchains to be ideal, as they not only just scale, but Appchains are also customisable and builder-friendly. Several projects have already launched their own Appchains, especially within the GameFi industry. Just consider that Blocklords, Super Champs, and Metacade are all launching Appchains while real-world services such as Proof 8 and MVL are doing the same thing.
Key Enhancement 3: Simplifying Onchain UX
Another very important recent enhancement is Smart Wallet Sub Accounts. This enhancement eliminates the need for multiple accounts by allowing users to manage all assets from one universal wallet. Therefore, this reduces friction by streamlining the on-chain experience with fewer signatures, all while making it easier to transfer assets between accounts. Smart Wallet Sub Accounts also enhanced security further by allowing users to fund new accounts directly from their universal wallet with spending permission. All of this is made possible by a new ERC standard which was developed by Base for hierarchical account ownership.
At this stage, it also makes sense to note that Base is actively preparing for the Pectra upgrade, which includes PeerDAS (Peer Data Availability Sampling) to enhance Ethereum’s data availability and ensure continued low-cost, scalable Layer 2 transactions. By collaborating with Ethereum core developers and contributing to protocol improvements, Base is reinforcing its commitment to scaling Ethereum while maintaining decentralisation and network efficiency.
If you are interested in understanding Ethereum’s next big upgrade, read our recent Pectra article here!
Base's Ecosystem
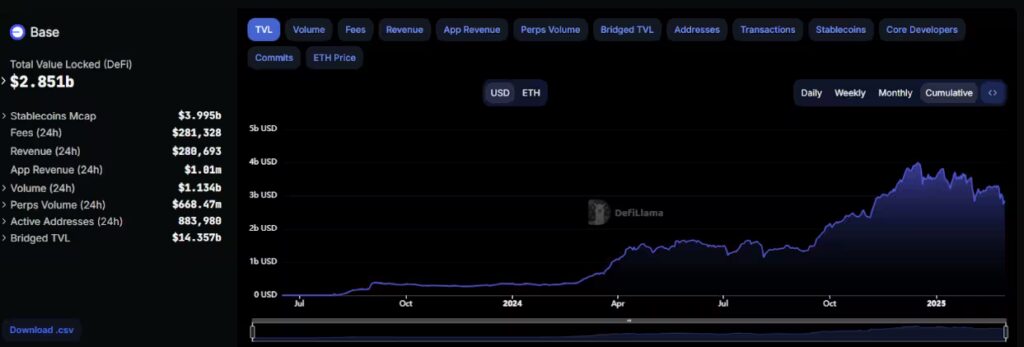
Although being a very young blockchain, Base rise has truly been meteoric, and this is particularly evident when considering metrics such as Total Value Locked (TVL) and the number of projects within its ecosystem. Consider that, at the time of writing, Base has a DeFi TVL of $2.8 Billion and has over 450 projects within its ecosystem. Let’s have a quick look at the top three projects on Base by TVL.
Aerodome Finance: Current TVL - $810 Million
Aerodrome Finance is a decentralised exchange (DEX) operating as the central liquidity hub on the Base network, and it makes use of a next-generation Automated Market Maker (AMM) design that combines a robust liquidity incentive mechanism with a vote-lock governance model to enhance user experience.
Morpho Blue: Current TVL - $410 Million
Morpho is a decentralised, non-custodial lending protocol that offers users the ability to lend and borrow digital assets securely and efficiently. Through its user-friendly interface, Morpho enables users to deposit assets into various vaults to earn interest based on their risk preferences. Additionally, Morpho provides flexible borrowing options, allowing users to borrow assets against their collateral with competitive interest rates and no extra fees.

AAVE V3: Current TVL - $398 Million
AAVE is one of the leading decentralised, non-custodial liquidity protocols within the blockchain space, and it is also active on Base. AAVE V3 enables users to supply and borrow various cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. Suppliers earn interest by providing liquidity to the market, while borrowers can access funds by posting collateral that exceeds the borrowed amount.
What is in Store for Base in 2025?
2025 promises to be a big year for Base with big goals. Consider that in a recent blog post, the project stated that by the end of 2025, it aims to have 25 million people using Base, aims to have 25 000 developers building on the blockchain, while also targeting a 250 Mgas/s blockspace capacity for increased scalability. Furthermore, Base also has the goal to have $100 billion in assets and also have 1 billion transactions!
To achieve these targets, Base layed out a five pillar strategy for 2025. Let’s have a quick look it!
Pillar 1: Base is for Builders
The first pillar of this strategy aims to empower developers with open tools to build world-class on-chain applications, by expanding the already capable OnchainKit and other developer resources. The project also plans to support gasless transactions via Paymasters and Layer 3 solutions, while at the same time, plans to ship new tools that will enable AI agents and mini-apps to interact seamlessly on-chain.
Pillar 2: Base is for Apps
The second pillar revolves around the plan to build an ecosystem of open, interconnected dApps to onboard more users. This may be done by improving app discoverability by expanding Base’s distribution network, while at the same time, enhancing creator monetisation through better tools and incentives. Additionally, the development of a core on-chain experience for social, trading, payment and messaging will also help to onboard even more users.
Pillar 3: Base is for Ownership
The next pillar focuses on a seamless on-chain identity system via Smart Wallets, which should result in a simplified onboarding process where users would be able to create and fund wallets in less than 60 seconds. This pillar also aims to eliminate complexity when managing on-chain assets and accounts, all while ensuring security and user privacy.
Pillar 4: Base is for Markets
The fourth pillar aims to position Base as the centre of the on-chain economy with liquid global markets. One of the goals here is to provide support to over 25 local stablecoins for seamless transactions in different regions while at the same time, expanding the on and off-ramps to make accessibility easy in every country.
Pillar 5: Base is for Everyone
Finally, the final pillar aims to scale the blockspace to 250 Mgas/s, aims to achieve Stage 1 decentralisation, removing the reliance on centralised components and further reducing transaction costs.
Conclusion
In a short amount of time, Base became one of the most important Layer 2 rollups for Ethereum and plans to further solidify its unique position by establishing a global onchain economy that fosters innovation, creativity, and freedom while envisioning a new internet built by the people, for the people.
We encourage everyone to delve deeper into Base, by exploring its ecosystem or if you are a developer, by helping to build an open, thriving on-chain economy. If you enjoyed this article, consider following Simply Staking on X by clicking here, so you won’t miss any of our upcoming articles!
Interested in Reading and Exploring Further? Consider the Below Links:
About Simply Staking
We are a Blockchain Services Provider who operates Validators and Nodes on over 30 Networks with over $1 Billion in Assets Staked. Our journey started in 2018, with Simply entering the Cosmos Hub Testnets, and now have expanded our operations to most major ecosystems including networks such as LIDO, Polygon, EigenLayer, Oasis Network, Cosmos Hub, Polkadot, and many more, all while being an Oracle Operator on Chainlink.
We offer additional services such as Nodes-As-A-Service (RPCs), Blockchain Development work, Tooling, Governance Services as well as Blockchain Consultancy Services.
More Information on our offerings can be found on our website.
Disclaimer: This article contains affiliate links. If you click on these links and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. These commissions help support our work and allow us to continue providing valuable content. Thank you for your support!
Terms & Conditions apply on all partnership offers.
This article is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Investing in cryptocurrencies carries significant risks and is highly speculative. The opinions and analyses presented do not reflect the official stance of any company or entity. We strongly advise consulting with a qualified financial professional before making any investment decisions. The author and publisher assume no liability for any actions taken based on the content of this article. Always conduct your own due diligence before investing.