This article introduces readers to the Polygon chain and offers a high-level overview of the corresponding ecosystem, including public and app chains, dApps, and decentralised ID.
What is Polygon?
Polygon (previously known as Matic Network) is a framework for building and connecting Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks. It aims to address some of Ethereum’s major limitations, such as low throughput, and high transaction fees by providing developers with tools to build scalable and efficient chains.
You might be interested in these articles:
Furthermore, Polygon employs a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to secure its sidechains (chains that run parallel to the polygon). Validators on the network are chosen based on the number of tokens they hold and are willing to stake as collateral, making the network secure and energy-efficient.
Polygon is often described as a Layer 2 (L2) scaling solution for Ethereum. L2 refers to protocols built on top of an existing blockchain (in this case, Ethereum) that improve its performance. L2s help offload some of the transactions from the Ethereum main chain, thereby reducing congestion and lowering fees.
As a next step, we explain L2 in more detail, since this framework is situated at the core of Polygon and will come up several times throughout the article.
What is a layer 2 blockchain?
Layer 2 (L2) blockchains are scaling solutions, generally constructed on top of Ethereum (L1), aimed at enhancing transaction throughput while maintaining decentralisation and security. Although L2s operate as independent chains, they are viewed as “extensions” of Ethereum. Users can directly submit transactions to L2 chains, which process them more efficiently in terms of cost and speed compared to Ethereum.
L2s bring scalability and efficiency by executing “batches” of transactions. Batching is a process of accumulating thousands of transactions and submitting them to Ethereum as a single transaction for final verification. Hence, L2s remove the burden of computational effort from L1, making the latter less congested
Typically, L2s deploy smart contracts (a piece of code that performs actions automatically) on Ethereum to handle the verification of transaction batches, ensuring their validity. Since the verification process takes place on Ethereum, meaning that Etehreum’s validators have a final say on the validity of teh transaction, L2s inherit the security of L1s.
The diagram below depicts the relationship between L1s and L2s.
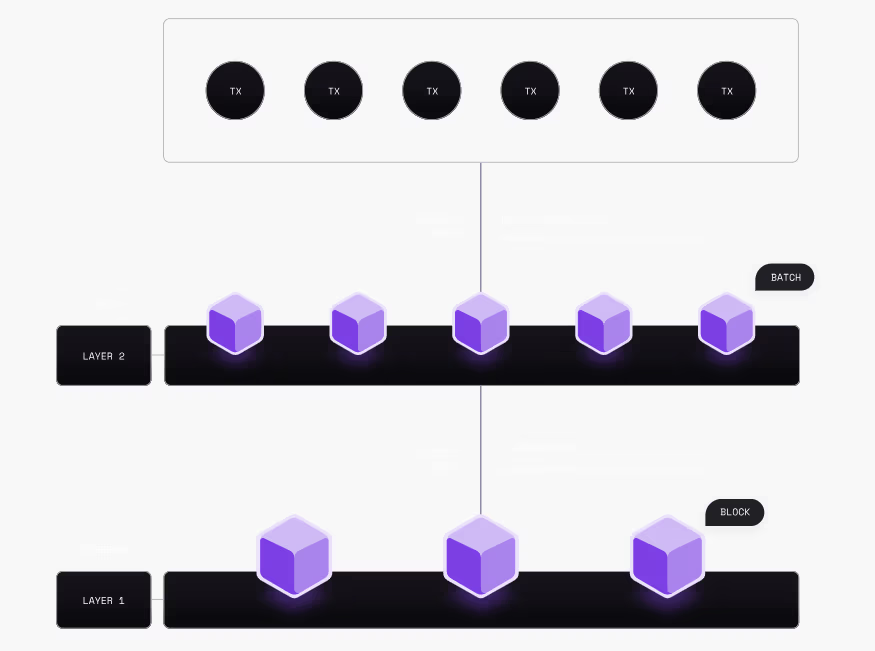
(Source: Polygon Docs)
L2s come in different shapes and sizes in terms of their relationship with Ethereum. Some L2s focus on scalability and trade-off security, while others aim for more decentralisation and higher levels of security. To capture different aspects of L2s, Polygon offers three main technology streams that fall into the following L2 categories:
- Public chains including Plygon PoS, Polygon zkEVM, and Polygon Miden
- Application chain called Polygon CDK
- Decentralised identity chain, known as Polygon ID
If these sound like a lot to digest, don’t worry! Below we guide you through each of the mentioned chains.
Public Chains
A public chain is a blockchain that is open and accessible to anyone, allowing any user to participate in the network in various ways including sending, receiving, or validating transactions.
Each of Polygon’s public chains has a specific focus, whether it’s enhancing scalability, security, or decentralisation for blockchain applications. Let’s start with Polygon PoS, followed by Polygon zkEVM, before reviewing Poygon Miden.
Polygon PoS
The Polygon Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network is designed to address scalability challenges within the Ethereum ecosystem. It operates as an L2 scaling solution for Ethereum, enhancing its throughput while lowering costs like transaction fees. Originally launched as Matic Network in June 2020, Polygon PoS has undergone numerous upgrades since its inception.
Nowadays, the Polygon PoS chain can process about 7,000 transactions per second, with transaction costs being as low as one cent. The network supports the development of decentralised applications (dApps), decentralised exchanges (DEXs), minting NFTs, and every other activity that can be performed on the Ethereum blockchain.
(Source: Polygon Docs)
The PoS chain is EVM compatible, meaning that Ethereum-based decentralised applications can be easily deployed without changing the original code. Because Polygon’s PoS can seamlessly work with the Ethereum blockchain, other standalone chains, and Layer-2 networks, assets can be transferred between the PoS chain and these networks.
Despite having reduced security, due to its reliance on a smaller set of validators compared to Ethereum, projects on the PoS chain accept this trade-off for faster, more efficient, and significantly cheaper transactions.
Polygon PoS remains as the foundational infrastructure for a wide array of decentralised applications and services.
Polygon zkEVM
Polygon zkEVM is an L2 network for Ethereum that uses zero-knowledge (ZK) technology to validate and quickly finalize off-chain transactions. It supports most Ethereum updates, precompiles (smart contracts that handle intensive tasks), and opcodes (code that performs basic operational tasks), allowing developers to deploy smart contracts, tools, and wallets used on Ethereum in a much cheaper environment.
Before exploring the benefits of zkEVM, let’s take a step back and explain how Polygon uses ZK technology to drive efficiency and scalability. ZK relies on a method where one party can prove to another that they know a piece of information without revealing the information itself, hence ensuring privacy and security in data verification.
By processing transactions off-chain, zkEVM can handle a higher volume of transactions at a lower cost and with greater speed compared to on-chain processing. Once these transactions are processed, zkEVM generates zero-knowledge proofs as proofs that confirm the transactions’ validity. These proofs are then submitted to the Ethereum blockchain, where they are verified. Via ZK proofs, Polygon zkEVM ensures that the transactions are valid and secure without needing to disclose all details such as amount and sender info, maintaining privacy and reducing the computational load on the Ethereum mainnet.
(Source: Polygon Docs)
Some of the benefits of zk EVM include:
- Low cost: As a sent outcome of harnessing ZK proofs, transaction costs are reduced, hence lowering the total cost of usage for end users for a better user experience.
- High performance: Fast network finality with frequent validity proofs based on ZKs, allows developers to create different types of dApps for a variety of user experiences.
- EVM equivalence: Being interoperable with EVM, means that developers can deploy their applications without code changes. Therefore, the majority of existing smart contracts, applications, and wallets work seamlessly across EVM, meaning that products can focus on enhancing user experience rather than spending resources on writing code.
- Security: Ethereum’s security is inherited in L2 with the additional benefit of L2 batching for scaling, meanwhile ZK proofs ensure transaction validity and safeguard user funds, guaranteeing that the stored information cannot be changed or corrupted.
Overall, Polygon zkEVM is an L2 solution that manages to offload computation overhead from Ethereum, lower costs for end users, and most importantly keep transaction information private and secure.
Polygon Miden
Polygon Miden is a technology that enhances Ethereum by processing many transactions at once and keeping them private, making it faster and more efficient for complex applications.
Comparatively speaking, Polygon Miden and Polygon zkEVM are both technologies designed to enhance Ethereum’s scalability using zero-knowledge proofs, but they have different approaches. Polygon zkEVM is built to be highly compatible with Ethereum, allowing developers to deploy their existing Ethereum smart contracts with minimal changes. It focuses on using zero-knowledge proofs to process and verify transactions off-chain while ensuring that all the necessary details are kept private and only the validity of transactions is confirmed on Ethereum.
Polygon Miden, on the other hand, is a more distinct approach that uses a different type of ZK technology known as STARKs (Scalable Transparent Arguments of Knowledge). It is designed to be highly efficient and secure, with a focus on enabling complex computations off-chain. This means that while Polygon zkEVM is geared towards compatibility and ease of use with existing Ethereum tools, Polygon Miden is more about expanding the range of operations beyond the Ethereum ecosystem and maintaining high security through its unique proof system.

(Source: Polygon Docs)
Polygon Miden, being available in the test version, has yet to become fully public and promises to bring several features, including:
- Enhanced Applications: Builders will be able to deploy Computational, data-heavy, or private applications with low costs and build privacy-first products like incomplete information games, and advanced wallets with hidden assets.
- High Throughput: Thanks to the Actor-based model, which is a way of organizing tasks where each “actor” works independently and handles their own part of the job, multiple tasks can be executed at the same time, hence increasing blockchain throughput.
- Full data & asset ownership: Users can decide what part of their data is to be disclosed on blockchain and build wallets that can change keys or be programmed to be recoverable.
You can learn more about Polygon Miden and its V3 Tesntent phase here.
Application Chain
AppChains, or application-specific blockchains, are designed to meet the unique requirements of a particular use case or business need. Unlike general-purpose blockchains, AppChains are optimized for specific functions, striving for more efficient processing, reduced congestion, and lower transaction costs
Polygon CDK
The Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK) is an open-source tool that helps developers build and set up different types of blockchain systems. It allows them to create new Layer 2 chains using Polygon zkEVM technology on Ethereum or eventually upgrade existing Layer 1 chains to use this technology.
Polygon CDK is modular, meaning that the toolkit is designed with separate, interchangeable parts or components. Such design allows developers to customise and build blockchain systems by adding or changing different parts of the CDK according to their needs, making the toolkit flexible and adaptable.

(Source: Polygon Docs)
Primary users of Polygon CDK are developers who can capitalise on the following features:
- EVM Compatibility: Out-of-the-box compatibility with existing Ethereum tooling, removing the need to need to change code.
- Customizable Components: Polygon CDK gives devs the freedom to build in a compliant way that suits users’ needs and aligns with business objectives.
- Native Gas Token: Allows users to have stable and predictable fees by using special “gas” tokens (tokens used to pay for transaction fees), while also giving chain operators the ability to adjust how fees are set to fit their needs.
Overall, Polygon CDK is like a wrench in a plumber’s toolkit, essential for getting the job done right. Polygon CDK is a flexible, customizable, and EVM-compatible kit that allows developers to build faster and at scale.
Decentralised Identity (DID)
Decentralised identity is a type of identity management that allows people to control their own digital identity without depending on a specific service provider. A digital identity is the body of information about an individual, organisation, or electronic device that exists online.
Polygon ID (Privado.ID)
Privado ID, previously known as Polygon ID, spun off from Polygon Labs to focus on the mainstream digital identity market and become a digital identity solution that enhances privacy and security using Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs).
Privado ID allows users to prove their identity without exposing personal data, hence being aligned with its mission to build trusted and secure relationships between users and dApps, following the principles of self-sovereign identity and privacy by default.
The solution behind Privado ID is built around three core components: the Identity Holder, Issuer, and Verifier, forming a trusted system for managing and verifying digital identities.
One of the key offerings of Privado ID is to simplify the process of confirming user identities via In-App Identity Verification. Instead of manually gathering verification data, users can rely on Privado ID to help them quickly obtain the necessary credentials.
Furthermore, Privado ID creates an identity wallet if needed, and handles verification directly within this wallet app, using Zero-Knowledge proofs for privacy. To help with understanding how in-wallet verification works, imagine doing a Know Your Customer (KYC) check within your DeFi wallet, where you submit your identity card, followed by a selfie. After submission, user data is encrypted (privately & securely stored) in the cloud and only decrypted on the user’s device.
What is more important, is that the submitted and verified credentials are reusable and can be stored in the Privado ID Wallet. Hence, in those applications where Privado ID is used as a verification mechanism – there is no need to go through the issuance and verification process again, hence allowing users to seamlessly access various apps.
Some real-world use cases of Privado ID include:
- Antibot / Sybil Attack: Customers can build content credibility in their social media platform, and ensure fair rewards distribution in Web3.
- Reusable eKYC: Protocols and/or businesses can undertake secure, seamless KYC for effortless compliance and privacy and verify identities privately to minimize risk.
- Age verification: Privado ID can be used to check and verify users’ age without revealing information to unauthorized 3rd parties, hence safeguarding minors, and privacy, and preventing fraud effortlessly.
Overall, Pirvado ID stands at the nexus of privacy and compliance and leverages blockchain technology to offer easy-to-use, reusable, and decentralised ID solutions.
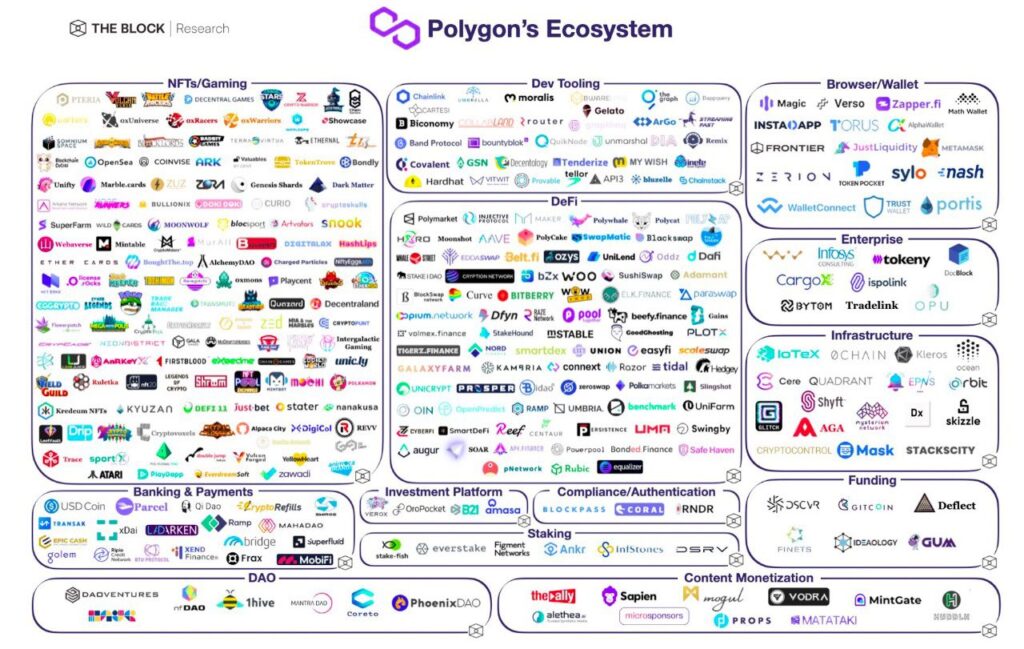
Ecosystem Overview
Polygon fosters a large and diversified ecosystem with sustainable growth. It includes 60+ dApps such as Aave – an open source and non-custodial liquidity protocol for earning interest on deposits and borrowing assets, and Ledger – one of the most private and secure non-custodial, hardware web3 wallets supporting all EVM networks.
Furthermore, 132 solution providers live on Polygon, such as OxPPL – a social network for web3, and Atato – a web3 custody solution for SMEs.
Last but not least, 35 Polygon ecosystem enablers include accelerators and venture capitals such as Bordelss Capital and Dune Ventures, supporting early-stage ecosystem projects and next-gen unicorns.
For a bird’s eye view of the ecosystem, see the map below and for a more detailed list, feel free to visit the Polygon Ecosystem page!
$POL (Ex-MATIC)
POL (Polygon Ecosystem Token), previously known as MATIC, is the main cryptocurrency of the Polygon ecosystem which enables users to interact with nearly all network participants and applications, as well as being used to secure the network via staking.
After migration from MATIC to POL is finalised on September 4th, POL will serve as the gas and staking token Polygon POS. Fortunately, this migration is seamless, meaning that MATIC holders on Polygon PoS do not need to take any action, however, those with MATIC tokens on Polygon zkEVM, Ethereum and centralised exchanges may need to undertake few simple steps. You can see Polygon’s official announcement for detailed information!
MATIC is essential for Polygon PoS. When users conduct transactions or use applications built on Polygon PoS, they pay a small fee in MATIC, which serves as an incentive for validators to process and verify the transactions.
As discussed, Polygon uses a proof-of-stake mechanism where staked MATIC is used to reach consensus on the network. By staking MATIC, users help secure Polygon PoS and can earn rewards. This system discourages validators from engaging in malicious behaviour. You can lay back and accumulate yield on your coins by delegating to Simply Staking via our networks page.
Additionally, Polygon validators implement Polygon Improvement Proposals (PIPs) and help with the decentralisation of Polygon PoS. MATIC is used to submit, fund, and vote on these PIPs.
For more information about the token, you can consult Etherscan and search for the POL token address: 0x455e53CBB86018Ac2B8092FdCd39d8444aFFC3F6
Polygon In Numbers
Polygon boasts a vibrant ecosystem with over 28,000 total contract creators driving innovation. It supports more than 219 million unique addresses, reflecting its expansive and growing user base. Moreover, the network has processed over 2.44 billion transactions by August 2024, demonstrating its high level of activity and efficiency. For example, in the NFT market alone, Polygon has facilitated over $12.80 billion in sales, showcasing its significant role in this space. The average cost per transaction on Polygon is approximately $0.015, highlighting the platform’s affordability while over 1.17 million deployed smart contracts underpin a wide array of applications, contributing to its innovative blockchain environment.
Conclusion
In summary, Polygon offers a practical solution for improving blockchain performance through several key technologies. It includes Polygon PoS, which enhances Ethereum by processing transactions more efficiently and at a lower cost, while Polygon zkEVM leverages zero-knowledge technology to speed up transactions and maintain privacy. Further, Polygon Miden focuses on handling complex computations efficiently, whilst Polygon ID provides a secure way for users to verify their identities without exposing personal details.
The Polygon ecosystem supports a range of applications and services, from deploying smart contracts to managing decentralised identities. Tools like the Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK) help developers build and customize blockchain systems, making it easier to create and manage new chains. Overall, Polygon’s approach helps address various challenges in blockchain technology, making it a practical choice for various use-cases.
Disclaimer: This article contains affiliate links. If you click on these links and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you. These commissions help support our work and allow us to continue providing valuable content. Thank you for your support!
This article is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as investment advice. Investing in cryptocurrencies carries significant risks and is highly speculative. The opinions and analyses presented do not reflect the official stance of any company or entity. We strongly advise consulting with a qualified financial professional before making any investment decisions. The author and publisher assume no liability for any actions taken based on the content of this article. Always conduct your own due diligence before investing.