Let’s try to visualise the entire cryptoverse as a geography map for a moment. What would it look like? Well, probably, as things stand, it would look like a bunch of isolated islands, all with their own thriving ecosystems but fundamentally disconnected from each other. Although blockchain ecosystems are expanding rapidly, interoperability remains a challenge. Cosmos set out to solve this issue by introducing the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) as a way to connect different blockchains together, but traditional IBC implementations still have inefficiencies.
So, what is the solution? Well, make the IBC better!
Union, the project that we will be discussing today, builds on the good work that was already done on IBC, but enhances it with a more flexible and efficient connection model by leveraging zero-knowledge proofs. Therefore, let’s dedicate some time to try and understand Union a bit deeper to see how it plans to solve the multi-chain fragmentation problem!
What is Union?

At a high level, Union may be described as a modular, next-generation interoperability protocol that is designed to connect Appchains, Layer 1s, and Layer 2s using a hyper-efficient zero-knowledge (zk) framework. Unlike traditional blockchain bridges that rely on centralised relayers or multi-signature mechanisms, Union leverages zero-knowledge proofs to provide a secure, scalable, and trust-minimised solution for cross-chain communication.
Understanding Union’s Protocol
First things first, it is fundamental for us to understand that Union builds on the IBC standard by introducing new key enhancements that help with efficiency, speed, and flexibility. It should be noted that in spite of the changes which make Union’s protocol different from the IBC protocol, Union is still fully compatible with IBC, and therefore allows for seamless communication with existing IBC-enabled chains. Think of Union as being IBC-compatible but optimised!
Moving on, to truly understand Union, one has to understand how Union facilitates cross-chain communication.
Connections and Channels
The project introduces a connection and channel model that is able to enhance the security and efficiency of blockchain interoperability. Ok, but what are connections and channels? Let’s try to define both of them in simple terms.
Connections
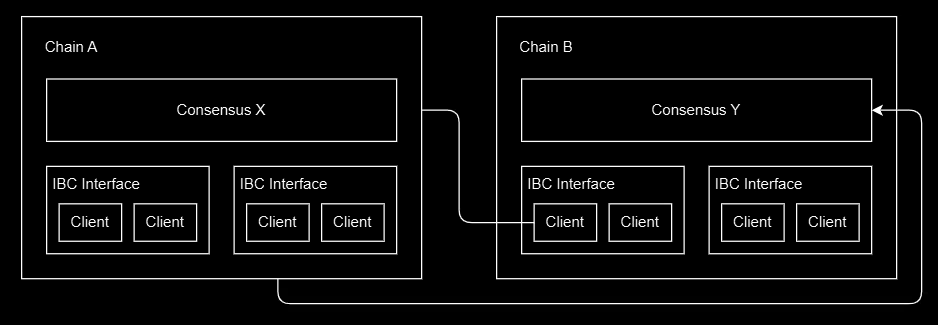
Connections in Union act as communication links between different blockchains, not only allowing them to exchange data and assets securely but also are able to define the security and finality of cross-chain interactions. This ensures that transactions sent between chains are verified correctly and finalised securely. Think of them as dedicated communications tunnels between two blockchains which allow for the exchange of secure and verifiable data between the two chains. Each of the two blockchains would keep track of its own list of connections, but the same connection will probably not have the same ID on both chains. Therefore, to solve this, Connection Identifiers (connection-id) are used. For example, blockchain A might have a connection-id set as “connection-15” that directly connects to blockchain B, which has the connection-id set as “connection-8”. Even though the IDs are different, they are actually connected because they have been confirmed as a valid connection pair, and therefore, they can open channels and transfer data or assets securely.
In simpler terms, connections establish a secure path so that the two blockchains can trust the data that they exchange while also ensuring that both blockchains verify each other’s transactions correctly. However, a connection alone does not send messages; it just makes sure that the two chains are linked securely. Connections are like a road that connects two cities. Just because a road exists doesn’t mean that cars are being driven on it, as the road is just the infrastructure needed, so if cars need to go from one city to the other, they would be able to. Very similarly, connections are the infrastructure needed to allow these transactions to occur between one blockchain and the other.
Channels
After connections between blockchains would have been secured, the blockchains would be able to open channels and start transfering data and assets securely between them. Channels in Union are able to organise and enode messages so that both blockchain can communicate in a structured way. Keeping the same analogy as in the previous section, think of channels as the lanes within a road that help organise the traffic, allowing a variety of data to be transferred securely and efficiently.
It is important to note that a single channel can run multiple protocol versions at the same time, meaning that different types of transitions can all coexist within the same channel. For example, the same channel is able to handle both a standard token transfer and NFT transfer at the same time. This is obviously very useful as it eliminates the need to open multiple channels for different types of messages while at the same time, it also simplifies cross-chain interactions.
Now that we have a good fundamental understanding of channels and connections let’s move on to discuss core components that may up Union.
Union’s Core Components
In this section we are going to explore Union’s core architecture, which is mainly made out of the following components: CometBLS, Galois and Voyager.
CometBLS
CometBLS is a consensus mechanism that is designed to make secure blockchain bridging more efficient by improving upon Tendermint. Tendermint is fast, but also makes it difficult to bridge with block space-limited chains like Ethereum for example, but by making zero-knowledge proofs cheaper and faster, CometBLS allows for better scalability. So what are CometBLS three key features?
BLS Signatures: Enabling efficient verification, BLS Signatures reduce the size of the transaction compared to ECDSA verification by aggregating signatures, meaning that less data would need to be transferred. This also allows for lower computation costs, as instead of verifying all the signatures, only the aggregated signatures need to be verified. Furthermore, zero-knowledge proof verification is also much faster, therefore making the entire bridging process more efficient. CometBLs is the main reason why Union is able to support and scale to hundred and thousands of validators without slowing down performance.
MiMC Hashing: The hashing algorithm used in Tendermint is the SHA-256. Within CometBLS, this is replaced with the MiMC hashing algorithm, which is more efficient in zero-knowledge circuits. Additionally, MiMC Hashing also improves the speed of proof generation while maintaining a high level of security.
Epoch-Based Validator Rotation: Inspired by Polkadot’s consensus and Cosmos’ governance and security models, Epoch-Based Validator Rotation reduces unnecessary updates to light clients, therefore making the system more cost-effective, while it also helps relayers save money and make the system cheaper for users.
In the future, CometBLS will incorporate Verkle Trees, a new way to store blockchain data by improving storage efficiency over Merkle Trees while efforts to reduce proving times and costs are ongoing.
Galoris
Galois is Union’s Zero-Knowledge (ZK) Consensus Proving system that ensures fast, low-cost, and censorship-resistant proof generation for blockchain consensus. Galoris key features are essentially 4.
Fast Proof Generation: Galoris can generate consensus proofs for 128 validators in 7 seconds, therefore ensuring quick bridging and a smooth user experience.
Low Cost: Unlike traditional ZK-proof systems that require expensive cloud computing, Galois is designed to be cheap and efficient.
Censorship-Resistant: Galoris allows anyone to generate proofs on their own machine while requiring only 5GB RAM to generate proofs for 128 validators, making it possible to run on entry-level consumer laptops.
Decentralised: Given that there is no need for complex cloud setups, anyone has the ability to operate a relayer or prover, increasing the number of possible participants in the system.
How Does Galoris work?
- Union sends an IBC packet.
- Galois generates a zero-knowledge proof of Union’s state at a specific block.
- The counterparty chain updates its state using the proof.
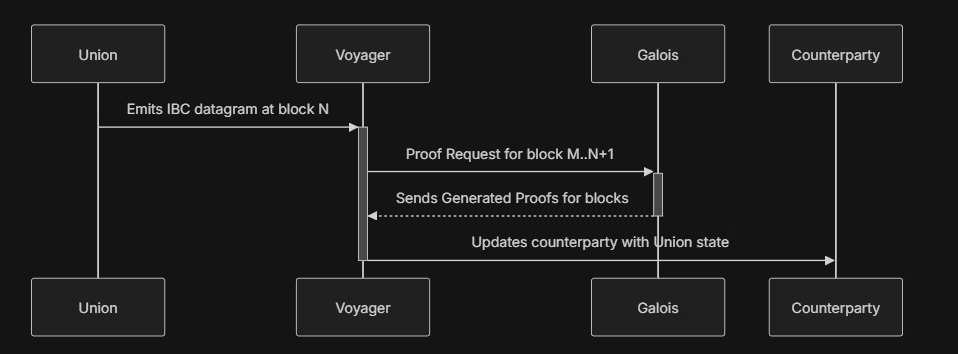
Galoris also plans to implement various improvements in the future. To learn more about Galoris and its future improvements, click here!
Voyager
Relaying transactions between blockchains is complex due to several key factors. First of all, consider that multiple relayers compete to submit transactions first, therefore leading to front-running issues. Data integrity is another point of consideration. Transactions must be submitted correctly as incorrect or missing packets can cause failure, especially in ordered channels while at the same time RPC failures are common, so relayers must recover quickly from crashes.
Voyager is Union’s advanced relayer that is able to solve all of these problems. It ensures reliability using a finite state machine model that allows for fast recovery, guaranteed data accuracy and parallel processing for increased speed and maximised efficiency.
Now that we have a good basic understanding of what Union is and how it works, let’s have a quick look at some recent development and what is in store in the near future.
Recent Development and Future Prospects
On December 3rd 2024, Union managed to raise $12 million in a Series A funding round, which Gumi Cryptos Capital and Longhash Ventures led, bringing the total capital raised by the project to $16 million. In late 2024, a partnership between Agoric and Union was announced with the goal to enhance cross-chain orchestration, and aiming to enable developers to create applications that can interact seamlessly across both Cosmos and EVM chains. More recently, in February 2025, Testnet 9, the final testnet before Union’s mainnet launch, went live and became open for public testing. For a detailed overview of all the new features included in the Union’s new testnet, click here to read more!
Following the successful deployment of Testnet 9, Union is actively preparing for its highly anticipated mainnet launch. This milestone marks a significant step toward delivering a secure, decentralised, and efficient interoperability solution for the blockchain ecosystem. The mainnet launch is expected to further enhance adoption, foster new integrations, and provide developers and users with a robust framework for interoperable blockchain applications.

It is also good to point out the ecosystem expansion, partnerships and collaboration that took place during 2024. Just to mention a few, Union has partnered with Stargaze to enable the transfer of blue-chip Ethereum NFTs to the Cosmos ecosystem and also started a collaboration with Native to develop trust-minimised interoperability solutions for the Bitcoin ecosystem. Union has also expanded its support to include Arbitrum, bringing zero-knowledge interoperability to Orbit chains. Additionally, Union’s partnership with Canto enables general message passing and asset transfers between Canto and IBC-enabled chains, and the project’s integration with XION aims to bring chain abstraction to dApps.
Conclusion
Union’s innovative approach to blockchain interoperability is setting a new standard in the industry, as by leveraging powerful technologies like zero-knowledge proofs and modular architecture, Union is paving the way for a more secure, decentralised, and scalable multi-chain ecosystem.
As the project moves closer to its mainnet launch, now is the perfect time to get involved and stay up-to-date with its progress. We encourage you to follow Simply Staking on X for the latest news and insights on Union and the broader blockchain ecosystem. Additionally, don’t miss out on the opportunity to participate in Union’s Testnet 9 and contribute to the final phase before mainnet goes live.
Join the movement today and help shape the future of blockchain interoperability!
Additional Resources
- Union Official Website: https://union.build/
- Union Testnet 9 Participation: https://app.union.build/
- Simply Staking on X: https://x.com/SimplyStaking
- Union Documentation: https://docs.union.build/
- Union Blog: https://union.build/blog