Crypto mass adoption – the promised land? It’s a phrase that any crypto native has been hearing over and over again as soon to become reality, but will it ever? One could argue that we are on the right track, especially when considering the continued rise of Bitcoin into pop culture by consolidating its narrative as at least being digital gold and by becoming the most sought-after asset on Wall Street.
Also Read these Articles from our NEAR Series:
But what about smart contract cryptocurrencies? The potential is certainly there, but to truly be adopted by the masses and not only by the crypto natives, a series of hurdles have to be overcome, starting with simplified UX/UI. An intuitive, seamless, and simplified user experience is fundamental to attracting the masses. Imagine a world where users could use a blockchain without even knowing it. Imagine no confusing wallet setups, no long wait times, and no sky-high gas fees. Well, imagine no longer. NEAR’s vision behind Chain Abstraction is exactly this, and that does not even cover all the other exciting ventures NEAR is tirelessly working on. Therefore, considering the project’s merits, we believe that NEAR deserves to be watched closely.
Let’s start our dive into NEAR!
What is NEAR Protocol?

NEAR Protocol is a blockchain that is built and designed to provide a user-friendly experience while at the same time, provide a scalable environment for developers to build on top of. From a technical standpoint, it is best to describe the project as a Layer 1, sharded, PoS carbon-neutral blockchain, built to be fast, secure, and scalable.
Initially conceptualised in 2017 by Illia Polosukhin and Alexander Skidano, the project was called NEAR.ai, and at first, it planned to develop a platform focused on machine learning and AI. In 2018, NEAR’s vision of providing developers with an easy solution for building dApps that could scale became clearer, and therefore, the project decided to build its own blockchain, which ultimately launched its mainnet in 2020. As NEAR started to grow, it also started to emphasise even more the importance of AI systems where users maintain ownership and control over their data and models. NEAR proudly sits at the intersection between blockchain and AI, with an ever greater commitment to innovation and addressing real-world challenges through technology.
Who are the Founders of the NEAR Protocol?
Illia Polosukhin: Mr. Polosukhin boasts over a decade of impressive industry experience, including a tenure at Google, where he contributed to TensorFlow and led a team building question-answering capabilities for the core of Google Search.
Alexander Skidano: Mr. Skidano started his career at Microsoft and later joined MemSQL (now SingleStore) as engineer number one, where he was responsible for building core features like storage, durability and sharding.
Now that we have a high-level understanding of what the project is about at its core, let’s start to understand it in more depth by discussing its key features.
Key Features of NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol’s key features are essentially four: NEAR’s AI integration and intelligent automation, Chain Abstraction, its user-friendly design, and its scalability and performance. Let’s discover them one by one starting with its user-friendly design.
Key Feature 1: AI Integration and Intelligent Automation
NEAR is one of the first blockchains that natively integrated Artificial Intelligence (AI), by fusing it within its blockchain, with a particular focus on decentralised intelligence and user-owned AI systems.
User-Owned AI Initiative

The project is clearly committed to creating an ecosystem where the users have ownership and full control not only over AI models but also over the data these models generate, hence reducing the reliance on centralised entities. In a blog post Mr. Polosukhin clearly outlines the project’s commitment to heavily invest in core infrastructure to support user-owned AI, including support to data collection and curation systems, access to computational resources and verifiable training and inference processes.
NEAR Intents: AI-Powered Transactions

In Q4 of 2024, NEAR Intents were announced. Essentially, NEAR Intents introduces a framework that allows AI agents, services, and users to exchange information, assets, and actions seamlessly while simplifying complex cross-chain interactions. In fact, NEAR Intents enables decentralised, cross-chain DeFi within an open and permissionless environment. One should also point out that by leveraging NEAR’s chain abstraction technology (we will be discussing this in the next section), NEAR Intents is able to seamlessly integrate a variety of blockchains without relying on traditional bridges, therefore reducing risks, costs, and wait times associated with cross-chain interactions. Another interesting key feature of NEAR Intents is Intent-Based Architecture. In practice, Intent-Based Architecture is able to replace traditional Automated Market Makers (AMM) models that require on-chain liquidity pools. Instead, NEAR Intents is able to operate on an intent-based model that requests quotes, which in turn, solvers (decentralised agents or entities within the NEAR Intent framework that execute and fulfil user-defined intents) fulfil dynamically. Effectively, this means better liquidity access for DeFi, CeFi and off-chain sources, which therefore leads to better prices. The final feature of NEAR Intents that we will be discussing is AccountFi. AccountFi is able to shift financial operations from individual token transactions to account-based interactions. In simple terms, this essentially means that instead of handling each token or asset separately, NEAR Intents allows users to manage entire accounts that contain multiple types of assets in one place.
For a deeper dive into NEAR Intents, click here!
Key Feature 2: Chain Abstraction
NEAR Intents are very important for the NEAR Protocol as they mark a fundamental technological innovation, but this is not the only innovation that clearly stands out. Chain Abstraction is certainly another, and therefore, it also deserves our attention.
The main intent behind Chain Abstraction is to simplify blockchain interactions, for example by allowing users to build applications without requiring extensive blockchain expertise, without the need to manage multiple wallets and also without having to deal with different networks to make use of a simple application. This is possible because of three core technologies that work together.
- NEAR Intents: This was discussed in the previous section.
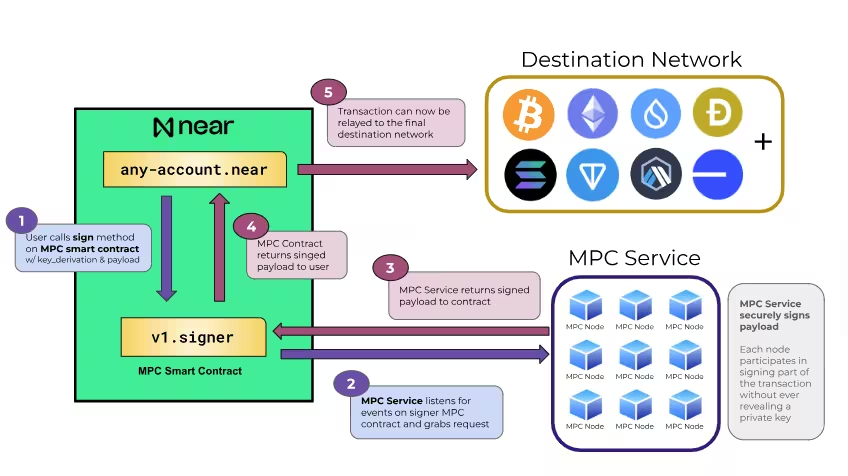
- Chain Signatures: This allows NEAR accounts, including smart contracts, to sign and execute transactions on other blockchains, which obviously facilitates cross-chain interactions by allowing a single NEAR account to manage assets and operations across multiple networks. In practice, Chain Signatures allows you to manage multiple blockchain interactions from one NEAR account while, at the same time, it also allows developers to write smart contracts on NEAR that are able to sign cross-chain transactions directly. Additionally, Chain Signatures allow for secure transaction signing and trustless signature generation by leveraging decentralised Multi-Party Computation (MPC),
What is MPC? Well it is a cryptographic technique that enables several parties to jointly compute a function without revealing their private inputs, ensuring security and privacy.
In simpler terms, consider that NEAR is able to interact both with Bitcoin’s UTXO model and Ethereum’s account model, enabling use cases such as cross-chain DeFi protocols, cross-chain atomic swaps, and cross-chain NFT marketplaces.
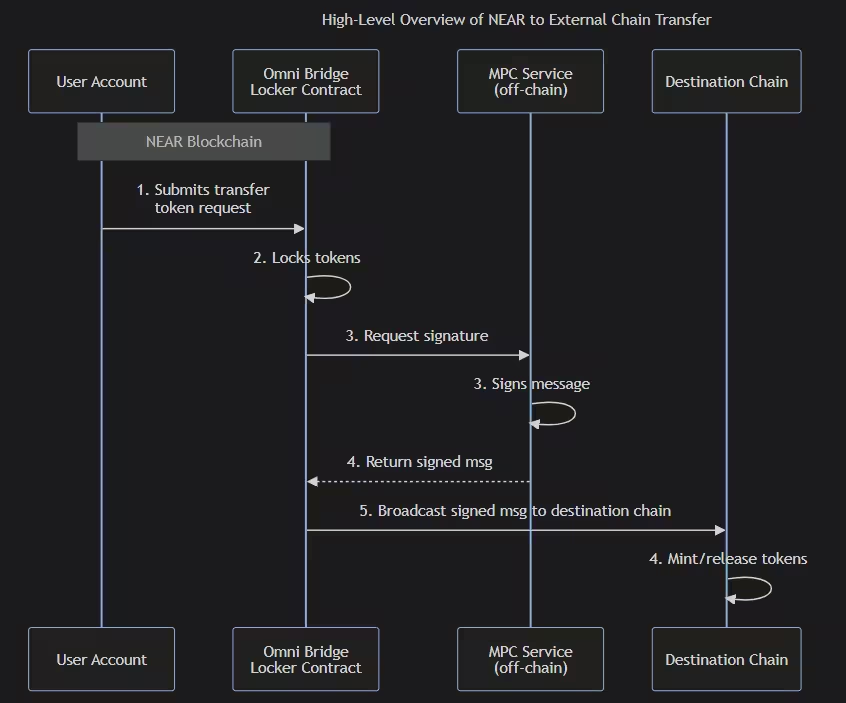
- OmniBridge: The OmniBridge is a multi-chain assets bridge that is able to combine Chain Signatures with chain-specific verification methods, therefore allowing for secure and efficient cross-chain transfers. The OmniBridge’s journey started with the Rainbow Bridge, a trustless cross-chain communication bridge enabling Ethereum-NEAR transfers. The main issue with the Rainbow Bridge was that it relied on NEAR light clients on Ethereum, which required high gas fees and complex validator tracking and also had long transaction times. The OmniBridge removes the need for light clients by making use of Chain Signatures and MPC services, which, in practice, means a reduction in verification times from hours to minutes while, at the same time, it results in lower gas costs across the supported chains.
Key Feature 3: User-Friendly Design
One of the main reasons why most blockchains have mostly failed to be adopted by the masses is technical complexity, and this is the first thing that NEAR Protocol is addressing. How? In multiple ways!
Human-Readable Accounts: Starting with the most basic, NEAR allows users to register human-readable account names (e.g. alice.NEAR), which makes transactions simpler and reduces the risk of errors. For example, consider that instead of sending crypto to 0x7f8d…, you send it to alice.NEAR. It is way more intuitive while, at the same time, it is a system that reduces the risks of making mistakes. No more triple-checking (or more) long strings of letters and numbers to make sure that the address is well written.
Fast Transactions and Low Fees: NEAR is able to achieve transaction finality in around one to two seconds, making it one of the quickest Layer 1 blockchains out there. This is possible because of Doomslug, which is a block-production mechanism that enables single-block finality by allowing validators to take turns producing blocks. A block is considered final once it has received signatures from more than half of the total stake, ensuring rapid finality in most cases. Additionally, the protocol has very cheap transaction fees!
To better visualise the key difference between Doomslug, and traditional dPoS mechanisms, consider the below table.
| Feature | Doomslug | dPoS |
| Block Production | Validators take turns producing blocks | In practice, a small set of delegates are responsible for producing blocks |
| Finality | Doomslug finality is reached in one round of communication, making blocks irreversible unless a participant is slashed. Full Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) finality occurs after two rounds | Finality is dependent on the elected delegates, meaning reorganisations (chain rollbacks) can occur |
| Consensus Participation | All validators participate in block production | Only a small number of delegates control block production |
| Security and Decentralisation | Requires more than half of validators to agree for Doomslug finality and 2/3 for BFT finality | A few large token holders can elect delegates, potentially leading to centralisation and collusion |
| Network Liveness | Continues producing and finalising blocks as long as over 50% of validators are online | Requires a majority of delegates to be active, making it vulnerable to coordination failures |
If you are interested in learning more about Doomslug, click here!
Key Feature 4: Scalability and Performance
NEAR’s unique approach to scalability and performance makes sure that the network always remains efficient even as user adoption grows. How is this possible you ask? Let’s see.
Nightshade Sharding for Scalability: The project makes use of this unique scaling solution that is able to split up the blockchain into multiple shards and therefore, allowing transactions to be processed in parallel. This differs from Ethereum for example, as NEAR is able to scale natively at the protocol level, therefore meaning that users do not have to rely on any rollups or sidechains.
Learn about this by reading Nightshade’s Whitepaper by clicking here.
High Throughput: The NEAR Protocol has a high throughput, meaning that it is able to process a very high number of transactions per second, making it much faster than Ethereum for example.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Consensus: The project is secured by a PoS consensus mechanism, which significantly reduces energy consumption and is, therefore, very environmentally friendly. At the time of writing, 232 active validators are securing NEAR’s blockchain, and Simply Staking is proudly one of them! Soon, we will also be launching our own staking dashboard for NEAR on our website. If you are interested in exploring other staking dashboards further for the time being, we encourage you to click here!
NEAR’s Metrics and Ecosystem
In an end-of-year blog post, Mr. Polosukhin gave a very interesting overview of the current state of the project, and provided some interesting metrics while also discussing NEAR’s ecosystem.
First of all, consider that at the time of writing that blog post (December 2024), the network was experiencing 40 million monthly active users (MAU), which marked an impressive increase of 7 million MAU in just one year. Even more impressive, a 4x increase was noted in daily active users over the previous year, and these users were responsible for conducting over 8 million daily transactions while having an average transaction fee of just $0.0002.
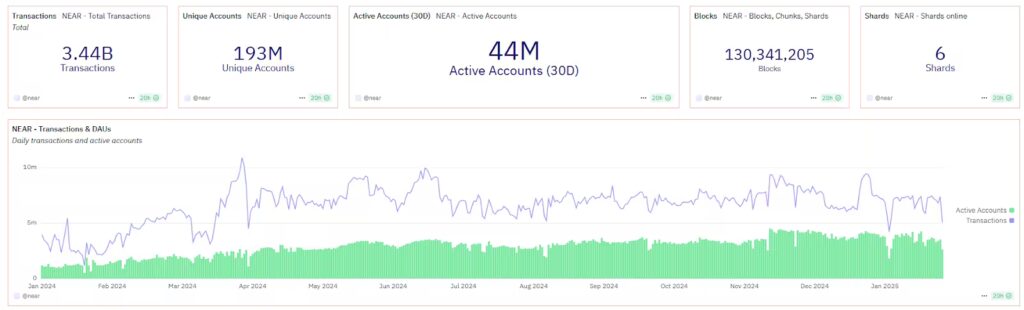
It is also very interesting to note that NEAR’s Protocol position as a leading blockchain for real-world applications was solidified, with four of the top Web3 apps by MAU built on NEAR. KAIKAI leads the pack with 31.7 million MAU, showcasing NEAR’s ability to support large-scale consumer applications while HOT Wallet, a widely used crypto wallet, boasts 4.2 million MAU. Additionally, SWEAT, a popular move-to-earn app, has 1.6 million MAU while Playember, a Web3 gaming platform has managed to attract 500k MAU.
Tokenomics: NEAR’s Economic Model
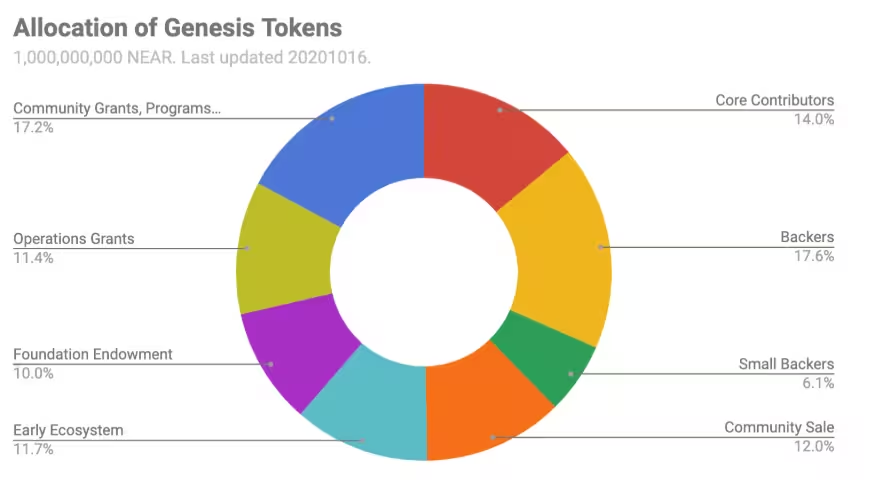
It is now time to delve into NEAR’s Tokenomics! First and foremost, it is important for us to understand that NEAR’s tokenomics were designed to foster sustainability and a community-driven ecosystem. At genesis, 1 billion NEAR tokens were minted and distributed as follows.
The following chart neatly represents the increase in circulating supply (the amount of tokens which are not subject to lockup periods) over time.
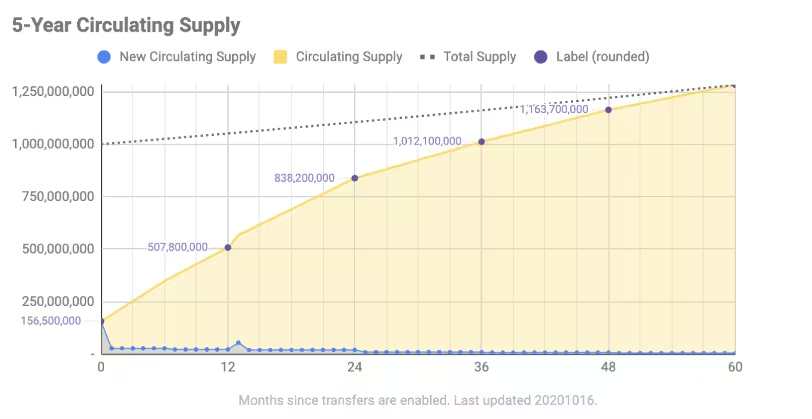
As you can notice, although at first, 1 billion NEAR tokens were minted, the tokens started to be released slowly over a period of time. Furthermore, it should also be noted that the protocol implements a 5% yearly inflation. Combining both, the protocol was able to estimate the following circulating and total supply of the NEAR token.
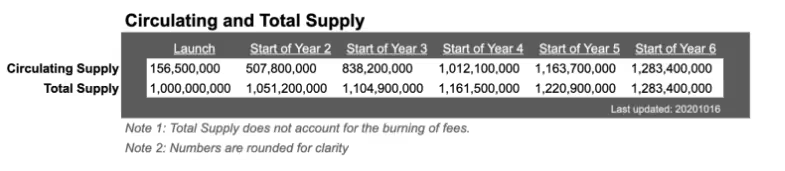
Another very important point to note is that 90% of the annual inflation (which would be equal to 4.5% of the total supply) is distributed to validators as a reward for securing the network, while the rest is allocated to the treasury of the protocol. Additionally, one should also point out that 70% of the transaction fees are burned, effectively reducing the total supply of the token over time. This means that as the network becomes more and more active, it could lead to an increase in deflationary pressure on the token supply. What happens to the rest of the 30% of the transaction fees you ask? The rest is allocated to the smart contracts that were involved in those transactions as a means of incentivising developers.
If you are interested in reading further, we encourage you to read both this and this.
Environmental Sustainability
One of NEAR’s biggest commitments is to sustainability, so much so that the blockchain has been certified to be carbon-neutral. A fun metric to consider is that the annual energy consumption of NEAR is equal to the energy used by Bitcoin in three minutes. Efficient indeed!
Consider delving deeper by reading about NEAR’s Climate Neutral Product Label award by clicking here!
Conclusion
NEAR has managed to establish itself as one of the leading platforms in the blockchain space by having a distinguished user-centric design, technological innovations and rapid ecosystem expansion. Both Chain Abstraction and AI Integration set NEAR apart from everything else. At the same time, these position the protocol as an important player in shaping the future of decentralised application, particularly at the intersection of blockchain and AI technologies.
We highly encourage you to delve deeper into NEAR Protocol, while also inviting you to follow Simply Staking on X by clicking here, for more content like this!
Interested in learning more? Check the following links out!
NEAR Doc: https://docs.NEAR.org/
NEAR Blog: https://NEAR.org/blog
NEAR Website: https://NEAR.org/